An acoustically controlled helical microrobot
- PMID: 37729400
- PMCID: PMC10511192
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adh5260
An acoustically controlled helical microrobot
Abstract
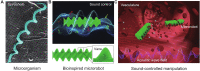
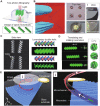
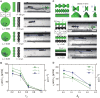
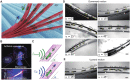
As a next-generation toolkit, microrobots can transform a wide range of fields, including micromanufacturing, electronics, microfluidics, tissue engineering, and medicine. While still in their infancy, acoustically actuated microrobots are becoming increasingly attractive. However, the interaction of acoustics with microstructure geometry is poorly understood, and its study is necessary for developing next-generation acoustically powered microrobots. We present an acoustically driven helical microrobot with a length of 350 μm and a diameter of 100 μm that is capable of locomotion using a fin-like double-helix microstructure. This microrobot responds to sound stimuli at ~12 to 19 kHz and mimics the spiral motion of natural microswimmers such as spirochetes. The asymmetric double helix interacts with the incident acoustic field, inducing a propulsion torque that causes the microrobot to rotate around its long axis. Moreover, our microrobot has the unique feature of its directionality being switchable by simply tuning the acoustic frequency. We demonstrate this locomotion in 2D and 3D artificial vasculatures using a single sound source.
Figures


References
-
- N. W. Charon, S. F. Goldstein, Genetics of motility and chemotaxis of a fascinating group of bacteria: The spirochetes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 36, 47–73 (2002). - PubMed
-
- C. Li, A. Motaleb, M. Sal, S. F. Goldstein, N. W. Charon, Spirochete periplasmic flagella and motility. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2, 345–354 (2000). - PubMed
-
- A. Ghosh, D. Dasgupta, M. Pal, K. I. Morozov, A. M. Leshansky, A. Ghosh, Helical nanomachines as mobile viscometers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28, 1705687 (2018).
-
- L. Zhang, J. J. Abbott, L. Dong, B. E. Kratochvil, D. Bell, B. J. Nelson, Artificial bacterial flagella: Fabrication and magnetic control. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 064107 (2009).
-
- X. Yan, Q. Zhou, M. Vincent, Y. Deng, J. Yu, J. Xu, T. Xu, T. Tang, L. Bian, Y.-X. J. Wang, K. Kostarelos, L. Zhang, Multifunctional biohybrid magnetite microrobots for imaging-guided therapy. Sci. Robot. 2, eaaq1155 (2017). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

