Single-cell genotypic and phenotypic analysis of measurable residual disease in acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 37729414
- PMCID: PMC10881057
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adg0488
Single-cell genotypic and phenotypic analysis of measurable residual disease in acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
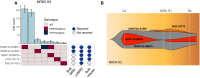
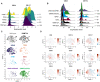
Measurable residual disease (MRD), defined as the population of cancer cells that persist following therapy, serves as the critical reservoir for disease relapse in acute myeloid leukemia and other malignancies. Understanding the biology enabling MRD clones to resist therapy is necessary to guide the development of more effective curative treatments. Discriminating between residual leukemic clones, preleukemic clones, and normal precursors remains a challenge with current MRD tools. Here, we developed a single-cell MRD (scMRD) assay by combining flow cytometric enrichment of the targeted precursor/blast population with integrated single-cell DNA sequencing and immunophenotyping. Our scMRD assay shows high sensitivity of approximately 0.01%, deconvolutes clonal architecture, and provides clone-specific immunophenotypic data. In summary, our scMRD assay enhances MRD detection and simultaneously illuminates the clonal architecture of clonal hematopoiesis/preleukemic and leukemic cells surviving acute myeloid leukemia therapy.
Figures




References
-
- H. Döhner, A. H. Wei, F. R. Appelbaum, C. Craddock, C. D. DiNardo, H. Dombret, B. L. Ebert, P. Fenaux, L. A. Godley, R. P. Hasserjian, R. A. Larson, R. L. Levine, Y. Miyazaki, D. Niederwieser, G. Ossenkoppele, C. Röllig, J. Sierra, E. M. Stein, M. S. Tallman, H.-F. Tien, J. Wang, A. Wierzbowska, B. Löwenberg, Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 ELN recommendations from an international expert panel. Blood 140, 2022, 1345–1377 - PubMed
-
- M. Heuser, S. D. Freeman, G. J. Ossenkoppele, F. Buccisano, C. S. Hourigan, L. L. Ngai, J. M. Tettero, C. Bachas, C. Baer, M. C. Béné, V. Bücklein, A. Czyz, B. Denys, R. Dillon, M. Feuring-Buske, M. L. Guzman, T. Haferlach, L. Han, J. K. Herzig, J. L. Jorgensen, W. Kern, M. Y. Konopleva, F. Lacombe, M. Libura, A. Majchrzak, L. Maurillo, Y. Ofran, J. Philippe, A. Plesa, C. Preudhomme, F. Ravandi, C. Roumier, M. Subklewe, F. Thol, A. A. van de Loosdrecht, B. A. van der Reijden, A. Venditti, A. Wierzbowska, P. J. M. Valk, B. L. Wood, R. B. Walter, C. Thiede, K. Döhner, G. J. Roboz, J. Cloos, 2021 update on MRD in acute myeloid leukemia: A consensus document from the European LeukemiaNet MRD Working Party. Blood 138, 2753–2767 (2021). - PMC - PubMed
-
- M. Terwijn, W. L. J. van Putten, A. Kelder, V. H. J. van der Velden, R. A. Brooimans, T. Pabst, J. Maertens, N. Boeckx, G. E. de Greef, P. J. M. Valk, F. W. M. B. Preijers, P. C. Huijgens, A. M. Dräger, U. Schanz, M. Jongen-Lavrecic, B. J. Biemond, J. R. Passweg, M. van Gelder, P. Wijermans, C. Graux, M. Bargetzi, M. C. Legdeur, J. Kuball, O. de Weerdt, Y. Chalandon, U. Hess, L. F. Verdonck, J. W. Gratama, Y. J. M. Oussoren, W. J. Scholten, J. Slomp, A. N. Snel, M. C. Vekemans, B. Löwenberg, G. J. Ossenkoppele, G. J. Schuurhuis, High prognostic impact of flow cytometric minimal residual disease detection in acute myeloid leukemia: Data from the HOVON/SAKK AML 42A study. J. Clin. Oncol. 31, 3889–3897 (2013). - PubMed
-
- D. Araki, B. L. Wood, M. Othus, J. P. Radich, A. B. Halpern, Y. Zhou, M. Mielcarek, E. H. Estey, F. R. Appelbaum, R. B. Walter, Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia: Time to move toward a minimal residual disease-based definition of complete remission? J. Clin. Oncol. 34, 329–336 (2016). - PMC - PubMed
-
- C. S. Hourigan, L. W. Dillon, G. Gui, B. R. Logan, M. Fei, J. Ghannam, Y. Li, A. Licon, E. P. Alyea, A. Bashey, H. J. Deeg, S. M. Devine, H. F. Fernandez, S. Giralt, M. Hamadani, A. Howard, R. T. Maziarz, D. L. Porter, B. L. Scott, E. D. Warlick, M. C. Pasquini, M. E. Horwitz, Impact of conditioning intensity of allogeneic transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia with genomic evidence of residual disease. J. Clin. Oncol. 38, 1273–1283 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

