Genome-Wide CRISPR Screens Identify Multiple Synthetic Lethal Targets That Enhance KRASG12C Inhibitor Efficacy
- PMID: 37729426
- PMCID: PMC10841254
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-2729
Genome-Wide CRISPR Screens Identify Multiple Synthetic Lethal Targets That Enhance KRASG12C Inhibitor Efficacy
Abstract
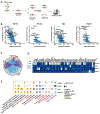
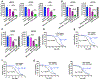
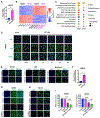
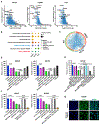
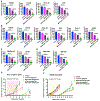
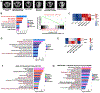
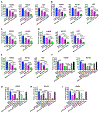
Non-small lung cancers (NSCLC) frequently (∼30%) harbor KRAS driver mutations, half of which are KRASG12C. KRAS-mutant NSCLC with comutated STK11 and/or KEAP1 is particularly refractory to conventional, targeted, and immune therapy. Development of KRASG12C inhibitors (G12Ci) provided a major therapeutic advance, but resistance still limits their efficacy. To identify genes whose deletion augments efficacy of the G12Cis adagrasib (MRTX-849) or adagrasib plus TNO155 (SHP2i), we performed genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 screens on KRAS/STK11-mutant NSCLC lines. Recurrent, potentially targetable, synthetic lethal (SL) genes were identified, including serine-threonine kinases, tRNA-modifying and proteoglycan synthesis enzymes, and YAP/TAZ/TEAD pathway components. Several SL genes were confirmed by siRNA/shRNA experiments, and the YAP/TAZ/TEAD pathway was extensively validated in vitro and in mice. Mechanistic studies showed that G12Ci treatment induced gene expression of RHO paralogs and activators, increased RHOA activation, and evoked ROCK-dependent nuclear translocation of YAP. Mice and patients with acquired G12Ci- or G12Ci/SHP2i-resistant tumors showed strong overlap with SL pathways, arguing for the relevance of the screen results. These findings provide a landscape of potential targets for future combination strategies, some of which can be tested rapidly in the clinic.
Significance: Identification of synthetic lethal genes with KRASG12C using genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 screening and credentialing of the ability of TEAD inhibition to enhance KRASG12C efficacy provides a roadmap for combination strategies. See related commentary by Johnson and Haigis, p. 4005.
©2023 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
All Roads Lead to Rome: YAP/TAZ Activity Influences Efficacy of KRASG12C Inhibitors.Cancer Res. 2023 Dec 15;83(24):4005-4007. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-3547. Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 38098448
References
-
- Bailey P, Chang DK, Nones K, Johns AL, Patch AM, Gingras MC, et al. Genomic analyses identify molecular subtypes of pancreatic cancer. Nature 2016;531:47–52 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

