Combination of an ACLY inhibitor with a GLP-1R agonist exerts additive benefits on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and hepatic fibrosis in mice
- PMID: 37729871
- PMCID: PMC10518624
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101193
Combination of an ACLY inhibitor with a GLP-1R agonist exerts additive benefits on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and hepatic fibrosis in mice
Abstract
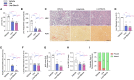
Increased liver de novo lipogenesis (DNL) is a hallmark of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). A key enzyme controlling DNL upregulated in NASH is ATP citrate lyase (ACLY). In mice, inhibition of ACLY reduces liver steatosis, ballooning, and fibrosis and inhibits activation of hepatic stellate cells. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonists lower body mass, insulin resistance, and steatosis without improving fibrosis. Here, we find that combining an inhibitor of liver ACLY, bempedoic acid, and the GLP-1R agonist liraglutide reduces liver steatosis, hepatocellular ballooning, and hepatic fibrosis in a mouse model of NASH. Liver RNA analyses revealed additive downregulation of pathways that are predictive of NASH resolution, reductions in the expression of prognostically significant genes compared with clinical NASH samples, and a predicted gene signature profile that supports fibrosis resolution. These findings support further investigation of this combinatorial therapy to treat obesity, insulin resistance, hypercholesterolemia, steatohepatitis, and fibrosis in people with NASH.
Keywords: ACLY; GLP-1R agonist; MASH; NAFLD; NASH; bempedoic acid; combination treatment; fatty acid metabolism; hepatic fibrosis; lipogenesis; liraglutide; mouse model; semaglutide.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests G.R.S. has received research funding from Esperion Therapeutics, Nestle, Cambrian Biosciences, Novo Nordisk, Poxel Pharmaceuticals, and Espervita Therapeutics; honoraria and/or consulting fees from Astra Zeneca, Cambrian Biosciences, Eli-Lilly, Esperion Therapeutics, Fibrocor Therapeutics, Poxel Therapeutics, and Merck; and is a founder and shareholder of Espervita Therapeutics. S.L.P. is an employee and shareholder of Esperion Therapeutics.
Figures



References
-
- Lazarus J.V., Mark H.E., Anstee Q.M., Arab J.P., Batterham R.L., Castera L., Cortez-Pinto H., Crespo J., Cusi K., Dirac M.A., et al. Advancing the global public health agenda for NAFLD: a consensus statement. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021;19:60–78. - PubMed
-
- Kleiner D.E., Brunt E.M., Van Natta M., Behling C., Contos M.J., Cummings O.W., Ferrell L.D., Liu Y.C., Torbenson M.S., Unalp-Arida A., et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2005;41:1313–1321. - PubMed
-
- Kim C.W., Addy C., Kusunoki J., Anderson N.N., Deja S., Fu X., Burgess S.C., Li C., Ruddy M., Chakravarthy M., et al. Acetyl CoA Carboxylase Inhibition Reduces Hepatic Steatosis but Elevates Plasma Triglycerides in Mice and Humans: A Bedside to Bench Investigation. Cell Metab. 2017;26:394–406.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.07.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

