Lenvatinib plus anti-PD-1 antibodies as conversion therapy for patients with unresectable intermediate-advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a single-arm, phase II trial
- PMID: 37730273
- PMCID: PMC10514649
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2023-007366
Lenvatinib plus anti-PD-1 antibodies as conversion therapy for patients with unresectable intermediate-advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a single-arm, phase II trial
Abstract
Background: Over 70% of the patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are diagnosed at an advanced stage and lose the opportunity for radical surgery. Combination therapy of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and anti-programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) antibodies has achieved a high tumor response rate in both the first-line and second-line treatment of advanced HCC. However, few studies have prospectively evaluated whether TKIs plus anti-PD-1 antibodies could convert unresectable intermediate-advanced HCC into resectable disease.
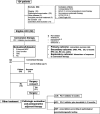
Methods: This single-arm, phase II study enrolled systemic therapy-naïve adult patients with unresectable Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage B or C HCC. Patients received oral lenvatinib one time per day plus intravenous anti-PD-1 agents every 3 weeks (one cycle). Tumor response and resectability were evaluated before the fourth cycle, then every two cycles. The primary endpoint was conversion success rate by investigator assessment. Secondary endpoints included objective response rate (ORR) by independent imaging review (IIR) assessment per modified RECIST (mRECIST) and Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors, V.1.1 (RECIST 1.1), progression-free survival (PFS) and 12-month recurrence-free survival (RFS) rate by IIR per mRECIST, R0 resection rate, overall survival (OS), and safety. Biomarkers were assessed as exploratory objectives.
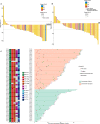
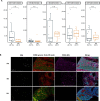
Results: Of the 56 eligible patients enrolled, 53 (94.6%) had macrovascular invasion, and 16 (28.6%) had extrahepatic metastasis. The median follow-up was 23.5 months. The primary endpoint showed a conversion success rate of 55.4% (31/56). ORR was 53.6% per mRECIST and 44.6% per RECIST 1.1. Median PFS was 8.9 months, and median OS was 23.9 months. Among the 31 successful conversion patients, 21 underwent surgery with an R0 resection rate of 85.7%, a pathological complete response rate of 38.1%, and a 12-month RFS rate of 47.6%. Grade ≥3 treatment-related adverse events were observed in 42.9% of patients. Tumor immune microenvironment analysis of pretreatment samples displayed significant enrichment of CD8+ T cells (p=0.03) in responders versus non-responders.
Conclusion: Lenvatinib plus anti-PD-1 antibodies demonstrate promising efficacy and tolerable safety as conversion therapy in unresectable HCC. Pre-existing CD8+ cells are identified as a promising biomarker for response to this regimen.
Trial registration number: Chinese Clinical Trial Registry, ChiCTR1900023914.
Keywords: Drug Therapy, Combination; Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors; Immunotherapy; Liver Neoplasms.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: ST, FZ, JC, SC, and XZ are employees of 3D Medicines Inc. Other authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phase Ib Study of Lenvatinib Plus Pembrolizumab in Patients With Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Clin Oncol. 2020 Sep 10;38(26):2960-2970. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.00808. Epub 2020 Jul 27. J Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32716739 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The impact of PD-1 inhibitors on prognosis in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated with TACE and lenvatinib: a retrospective study.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 21;14(1):14334. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63571-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38906915 Free PMC article.
-
A real-world study of the efficacy of second-line treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with esophagogastric varices after progression on first-line lenvatinib combined with PD-1 inhibitor.World J Surg Oncol. 2025 Mar 13;23(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12957-025-03742-0. World J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40082982 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of transarterial chemoembolization combined with lenvatinib and PD-1 inhibitor in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis.Pharmacol Ther. 2024 May;257:108634. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2024.108634. Epub 2024 Mar 16. Pharmacol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38499069 Review.
-
Systemic conversion therapies for initially unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2024 Aug 14;24(1):1008. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12772-y. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39143584 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Targeting STING signaling for the optimal cancer immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 9;15:1482738. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1482738. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39450170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cure can be achieved by conversion to microwave ablation following atezolizumab-bevacizumab therapy in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.J Liver Cancer. 2024 Sep;24(2):234-242. doi: 10.17998/jlc.2024.05.23. Epub 2024 Jun 3. J Liver Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38825875 Free PMC article.
-
A Metrology Informatics Investigation of Conversion Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2014-2023.Ann Surg Open. 2025 Mar 12;6(1):e562. doi: 10.1097/AS9.0000000000000562. eCollection 2025 Mar. Ann Surg Open. 2025. PMID: 40134489 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Metabolism: Innovative Therapies for MASLD Unveiled.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 25;26(9):4077. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094077. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of survival benefit and safety profile between lenvatinib and donafenib as conversion therapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Am J Transl Res. 2025 May 15;17(5):3496-3504. doi: 10.62347/PBLA2928. eCollection 2025. Am J Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40535653 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
