One-Lung Ventilation and Postoperative Pulmonary Complications After Major Lung Resection Surgery. A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 37730455
- PMCID: PMC10133024
- DOI: 10.1053/j.jvca.2023.04.029
One-Lung Ventilation and Postoperative Pulmonary Complications After Major Lung Resection Surgery. A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Objectives: The effect of one-lung ventilation (OLV) strategy based on low tidal volume (TV), application of positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), and alveolar recruitment maneuvers (ARM) to reduce postoperative acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and pulmonary complications (PPCs) compared with higher TV without PEEP and ARM strategy in adult patients undergoing lobectomy or pneumonectomy has not been well established.
Design: Multicenter, randomized, single-blind, controlled trial.
Setting: Sixteen Italian hospitals.
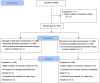
Participants: A total of 880 patients undergoing elective major lung resection.
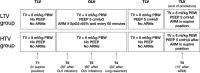
Interventions: Patients were randomized to receive lower tidal volume (LTV group: 4 mL/kg predicted body weight, PEEP of 5 cmH2O, and ARMs) or higher tidal volume (HTL group: 6 mL/kg predicted body weight, no PEEP, and no ARMs). After OLV, until extubation, both groups were ventilated using a tidal volume of 8 mL/kg and a PEEP value of 5 cmH2O. The primary outcome was the incidence of in-hospital ARDS. Secondary outcomes were the in-hospital rate of PPCs, major cardiovascular events, unplanned intensive care unit (ICU) admission, in-hospital mortality, ICU length of stay, and in-hospital length of stay.
Measurements and main results: ARDS occurred in 3 of 438 patients (0.7%, 95% CI 0.1-2.0) and in 1 of 442 patients (0.2%, 95% CI 0-1.4) in the LTV and HTV group, respectively (Risk ratio: 3.03 95% CI 0.32-29, p = 0.372). Pulmonary complications occurred in 125 of 438 patients (28.5%, 95% CI 24.5-32.9) and in 136 of 442 patients (30.8%, 95% CI 26.6-35.2) in the LTV and HTV group, respectively (risk ratio: 0.93, 95% CI 0.76-1.14, p = 0.507). The incidence of major complications, in-hospital mortality, and unplanned ICU admission, ICU and in-hospital length of stay were comparable in both groups.
Conclusions: In conclusion, among adult patients undergoing elective lung resection, an OLV with lower tidal volume, PEEP 5 cmH2O, and ARMs and a higher tidal volume strategy resulted in low ARDS incidence and comparable postoperative complications, in-hospital length of stay, and mortality.
Keywords: acute lung injury; anesthesia; complications, postoperative; one-lung ventilation; respiratory distress syndrome, adults; thoracic surgery.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest None.
Figures

Comment in
-
Protective Lung Ventilation: What Do We Know?-"In An Investigation, Details Matter"-Jack Reacher TV Series.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2023 Dec;37(12):2572-2576. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2023.06.018. Epub 2023 Jun 14. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2023. PMID: 37423839 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

