Gastric insufflation and surgical view according to mask ventilation method for laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomized controlled study
- PMID: 37730575
- PMCID: PMC10510126
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-023-02269-9
Gastric insufflation and surgical view according to mask ventilation method for laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomized controlled study
Abstract
Background: Proper mask ventilation is important to prevent air inflow into the stomach during induction of general anesthesia, and it is difficult to send airflow only through the trachea without gastric inflation. Changes in gastric insufflation according to mask ventilation during anesthesia induction were compared.
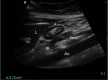
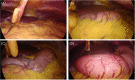
Methods: In this prospective, randomized, single-blind study, 230 patients were analyzed to a facemask-ventilated group (Ventilation group) or no-ventilation group (Apnea group) during anesthesia induction. After loss of consciousness, pressure-controlled ventilation at an inspiratory pressure of 15 cmH2O was performed for two minutes with a two-handed mask-hold technique for Ventilation group. For Apnea group, only the facemask was fitted to the face for one minute with no ventilation. Next, endotracheal intubation was performed. The gastric cross-sectional area (CSA, cm2) was measured using ultrasound before and after induction. After pneumoperitoneum with carbon dioxide, gastric insufflation of the surgical view was graded by the surgeon for each group.
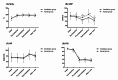
Results: Increase of postinduction antral CSA on ultrasound were not significantly different between Ventilation group and Apnea group (0.04 ± 0.3 and 0.02 ± 0.28, p-value = 0.225). Additionally, there were no significant differences between the two groups in surgical grade according to surgeon's judgement.
Conclusions: Pressure-controlled ventilation at an inspiratory pressure of 15 cmH2O for two minutes did not increase gastric antral CSA and insufflation of stomach by laparoscopic view.
Trial registration: http://cris.nih.go.kr (KCT0003620) on 13/3/2019.
Keywords: Anesthesia induction; Gastric antral cross-sectional area; Gastric insufflation; Gastric ultrasound; Laparoscopy; Rapid sequence induction.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Determination of the optimal inspiratory pressure providing adequate ventilation while minimizing gastric insufflation using real-time ultrasonography in Chinese children: a prospective, randomized, double-blind study.BMC Anesthesiol. 2017 Sep 11;17(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s12871-017-0417-0. BMC Anesthesiol. 2017. PMID: 28893201 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of facemask oxygenation with and without positive pressure ventilation on gastric volume during anesthesia induction in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy or partial hepatectomy: a randomized controlled trial.BMC Anesthesiol. 2022 Dec 30;22(1):412. doi: 10.1186/s12871-022-01958-1. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022. PMID: 36581835 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation of adequacy of ventilation and gastric insufflation at three levels of inspiratory pressure for facemask ventilation during induction of anaesthesia: A randomised controlled trial.Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. 2022 Oct;41(5):101132. doi: 10.1016/j.accpm.2022.101132. Epub 2022 Jul 25. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. 2022. PMID: 35901954 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of facemask ventilation with different ventilating volumes on gastric insufflation during anesthesia induction in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy.Saudi Med J. 2019 Oct;40(10):989-995. doi: 10.15537/smj.2019.10.24306. Saudi Med J. 2019. PMID: 31588476 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time detection of gastric insufflation related to facemask pressure-controlled ventilation using ultrasonography of the antrum and epigastric auscultation in nonparalyzed patients: a prospective, randomized, double-blind study.Anesthesiology. 2014 Feb;120(2):326-34. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000094. Anesthesiology. 2014. PMID: 24317204 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Bouvet L, Albert ML, Augris C, Boselli E, Ecochard R, Rabilloud M, et al. Real-time detection of gastric insufflation related to facemask pressure-controlled ventilation using ultrasonography of the antrum and epigastric auscultation in nonparalyzed patients: a prospective, randomized, double-blind study. Anesthesiology. 2014;120:326–34. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000094. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

