Evidence for a metacognitive awareness of autobiographical memory organisation
- PMID: 37730715
- PMCID: PMC10511418
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-34389-0
Evidence for a metacognitive awareness of autobiographical memory organisation
Abstract
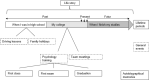
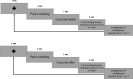
Models of autobiographical memory (AM) recall posit some form of control process, but the extent to which we can reflect on this form of retrieval is under-researched. Here we propose a method for measuring such metacognitive awareness in AM. Since the verification of personal facts is difficult, we based our design on AM organisation. AMs are proposed to be organised into a coherent life story, that is, a subjective chronology reflecting the goals of the individual over time. We investigated the metacognitive awareness of this coherence. Eighty-three participants generated AMs and made two judgements of order for pairs of memories and gave a confidence rating. We found that participants were indeed able to distinguish pairs of memories that were coherent with their life story chronology from pairs which were not. We also found a significant effect of response time and task difficulty on confidence, suggesting that judgement of order fluency was determinant for metacognitive evaluation. This suggests common properties between metacognitive abilities related to autobiographical memory and those related to other forms of memory.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metacognitive processes accompanying the first stages of autobiographical retrieval in the self-memory system.Memory. 2024 Jul;32(6):776-789. doi: 10.1080/09658211.2024.2370532. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Memory. 2024. PMID: 38963905
-
The effect of impaired verbal memory retrieval on autobiographical memory across different life periods in schizophrenia.Compr Psychiatry. 2018 Jan;80:81-88. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2017.09.002. Epub 2017 Sep 12. Compr Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29069623
-
The phenomenology of autobiographical retrieval.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Cogn Sci. 2023 May-Jun;14(3):e1638. doi: 10.1002/wcs.1638. Epub 2022 Dec 2. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Cogn Sci. 2023. PMID: 36458642 Review.
-
Autobiographical memory in schizophrenia: The role of metacognition.Compr Psychiatry. 2021 Aug;109:152254. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2021.152254. Epub 2021 Jun 17. Compr Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34174693
-
[Episodic autobiographical memory in depression: a review].Encephale. 2006 Oct;32(5 Pt 1):781-8. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(06)76231-5. Encephale. 2006. PMID: 17099603 Review. French.
References
-
- Nelson T, Narens L. Metamemory: A theoretical framework and new findings. Psychol. Learn. Motiv. 1990;26:125–173. doi: 10.1016/S0079-7421(08)60053-5. - DOI
-
- Mazzoni G, Hanczakowski M. Metacognitive processes before and during Retrieval. In: Higham P, Leboe J, editors. Constructions of Remembering and Metacognition: Essays in Honour of Bruce Whittlesea. Palgrave Macmillan; 2011. pp. 91–106.
-
- Mazzoni G, Kirsch I. Autobiographical memories and beliefs: A preliminary metacognitive model. In: Perfect TJ, Schwartz BL, editors. Applied Metacognition. Cambridge University Press; 2002. pp. 121–145.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

