Immunomodulatory contribution of mast cells to the regenerative biomaterial microenvironment
- PMID: 37730736
- PMCID: PMC10511634
- DOI: 10.1038/s41536-023-00324-0
Immunomodulatory contribution of mast cells to the regenerative biomaterial microenvironment
Abstract
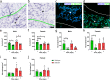
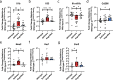
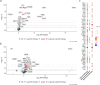
Bioactive immunomodulatory biomaterials have shown promise for influencing the immune response to promote tissue repair and regeneration. Macrophages and T cells have been associated with this response; however, other immune cell types have been traditionally overlooked. In this study, we investigated the role of mast cells in the regulation of the immune response to decellularized biomaterial scaffolds using a subcutaneous implant model. In mast cell-deficient mice, there was dysregulation of the expected M1 to M2 macrophage transition typically induced by the biomaterial scaffold. Polarization progression deviated in a sex-specific manner with an early transition to an M2 profile in female mice, while the male response was unable to properly transition past a pro-inflammatory M1 state. Both were reversed with adoptive mast cell transfer. Further investigation of the later-stage immune response in male mice determined a greater sustained pro-inflammatory gene expression profile, including the IL-1 cytokine family, IL-6, alarmins, and chemokines. These results highlight mast cells as another important cell type that influences the immune response to pro-regenerative biomaterials.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
K.L.C. is a co-founder, consultant, board member, and holds an equity interest in Ventrix Bio, Inc, and is an Editor-in-Chief of
Figures



References
-
- Christy AL, Brown MA. The multitasking mast cell: positive and negative roles in the progression of autoimmunity. J. Immunol. 2007;179:2673. - PubMed
-
- Amin K. The role of mast cells in allergic inflammation. Respir. Med. 2012;106:9–14. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharya K, et al. Mast cell deficient W/Wv mice have lower serum IL-6 and less cardiac tissue necrosis than their normal littermates following myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharm. 2007;20:69–74. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

