The anti-cancer effect of epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate against multiple myeloma cells is potentiated by 5,7-dimethoxyflavone
- PMID: 37730921
- PMCID: PMC10626272
- DOI: 10.1002/2211-5463.13708
The anti-cancer effect of epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate against multiple myeloma cells is potentiated by 5,7-dimethoxyflavone
Abstract
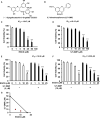
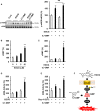
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate (EGCG) is one of the major components of green tea polyphenol. Previous studies have shown that EGCG induces cancer-specific cell death in vitro and in vivo without causing severe side effects. However, the anti-cancer effect of EGCG alone is limited. 5,7-dimethoxyflavone (5,7-DMF), one of the principal functional components of black ginger (Kaempferia parviflora), also exerts anti-cancer effects. Here, we show that 5,7-DMF synergistically enhances the anti-cancer effect of EGCG in multiple myeloma cells by potentiating EGCG-induced intracellular cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) production. Moreover, the combination of EGCG and 5,7-DMF induces apoptotic cell death in multiple myeloma cells, and this is accompanied by activation of the cGMP/acid sphingomyelinase (ASM)/cleaved caspase-3 pathway. In conclusion, we have shown that 5,7-DMF enhances the anti-cancer effect of EGCG by upregulating cGMP in multiple myeloma cells.
Keywords: (−)-epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate; 5,7-dimethoxyflavone; acid sphingomyelinase; cyclic guanosine monophosphate; multiple myeloma.
© 2023 The Authors. FEBS Open Bio published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hydrogen sulphide donors selectively potentiate a green tea polyphenol EGCG-induced apoptosis of multiple myeloma cells.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 27;7(1):6665. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-06879-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28751723 Free PMC article.
-
Epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate induces acid sphingomyelinase activation through activation of phospholipase C.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019 Nov 26;520(1):186-191. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.09.102. Epub 2019 Oct 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019. PMID: 31585731
-
Fustin, a Flavanonol, Synergically Potentiates the Anticancer Effect of Green Tea Catechin Epigallocatechin-3-O-Gallate with Activation of the eNOS/cGMP Axis.J Agric Food Chem. 2022 Mar 23;70(11):3458-3466. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c07567. Epub 2022 Feb 25. J Agric Food Chem. 2022. PMID: 35212538
-
Therapeutic Effects of Green Tea Polyphenol (‒)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) in Relation to Molecular Pathways Controlling Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 25;24(1):340. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010340. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) as adjuvant in cancer therapy.Clin Nutr. 2013 Dec;32(6):894-903. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2013.03.008. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Clin Nutr. 2013. PMID: 23582951 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic Variations in Bamboo Shoot Boiled Liquid During Pediococcus pentosaceus B49 Fermentation.Foods. 2025 Aug 5;14(15):2731. doi: 10.3390/foods14152731. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40807668 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer Activity of Ether Derivatives of Chrysin.Molecules. 2025 Feb 19;30(4):960. doi: 10.3390/molecules30040960. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40005270 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Naganuma T, Kuriyama S, Kakizaki M, Sone T, Nakaya N, Ohmori‐Matsuda K, Hozawa A, Nishino Y and Tsuji I (2009) Green tea consumption and hematologic malignancies in Japan: the Ohsaki study. Am J Epidemiol 170, 730–738. - PubMed
-
- Bettuzzi S, Brausi M, Rizzi F, Castagnetti G, Peracchia G and Corti A (2006) Chemoprevention of human prostate cancer by oral administration of green tea catechins in volunteers with high‐grade prostate intraepithelial neoplasia: a preliminary report from a one‐year proof‐of‐principle study. Cancer Res 66, 1234–1240. - PubMed
-
- Tachibana H, Koga K, Fujimura Y and Yamada K (2004) A receptor for green tea polyphenol EGCG. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11, 380–381. - PubMed
-
- Tsukamoto S, Yamashita S, Kim YH, Kumazoe M, Huang Y, Yamada K and Tachibana H (2012) Oxygen partial pressure modulates 67‐kDa laminin receptor expression, leading to altered activity of the green tea polyphenol, EGCG. FEBS Lett 586, 3441–3447. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

