Tumor microenvironment-mediated immune profiles and efficacy of anti-PD-L1 antibody plus chemotherapy stratified by DLL3 expression in small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 37731022
- PMCID: PMC10703835
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-023-02427-3
Tumor microenvironment-mediated immune profiles and efficacy of anti-PD-L1 antibody plus chemotherapy stratified by DLL3 expression in small-cell lung cancer
Erratum in
-
Correction: Tumor microenvironment-mediated immune profiles and efficacy of anti-PD-L1 antibody plus chemotherapy stratified by DLL3 expression in small-cell lung cancer.Br J Cancer. 2023 Dec;129(12):2034. doi: 10.1038/s41416-023-02481-x. Br J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37923915 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Delta-like ligand 3 (DLL3) is a therapeutic target in small-cell lung cancer (SCLC). However, how DLL3 expression status affects the tumor microenvironment (TME) and clinical outcomes in SCLC remains unclear.
Methods: This retrospective study included patients with postoperative limited-stage (LS)-SCLC and extensive-stage (ES)-SCLC treated with platinum and etoposide (PE) plus anti-programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) antibody. We investigated the relationship of DLL3 expression with TME, mutation status, tumor neoantigens, and immunochemotherapy.
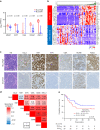
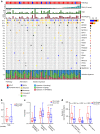
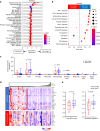
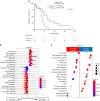
Results: In the LS-SCLC cohort (n = 59), whole-exome sequencing revealed that DLL3High cases had significantly more neoantigens (P = 0.004) and a significantly higher rate of the signature SBS4 associated with smoking (P = 0.02) than DLL3Low cases. Transcriptome analysis in the LS-SCLC cohort revealed that DLL3High cases had significantly suppressed immune-related pathways and dendritic cell (DC) function. SCLC with DLL3High had significantly lower proportions of T cells, macrophages, and DCs than those with DLL3Low. In the ES-SCLC cohort (n = 30), the progression-free survival associated with PE plus anti-PD-L1 antibody was significantly worse in DLL3High cases than in DLL3Low cases (4.7 vs. 7.4 months, P = 0.01).
Conclusions: Although SCLC with DLL3High had a higher neoantigen load, these tumors were resistant to immunochemotherapy due to suppressed tumor immunity by inhibiting antigen-presenting functions.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. TY reports grants from Takeda, Daiichi-Sankyo, AbbVie, and Bristol-Myers Squibb; grants and personal fees from Ono, Novartis, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Amgen; and personal fees from AstraZeneca. KK reports personal fees from Chugai, ArcherDX, Eli Lilly, Roche, and Taiho outside the submitted work. Dr. YM reports grants from Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas, Hitachi, Ltd., the National Cancer Center Research and Development Fund, and Olympus, and personal fees from AstraZeneca. Drs. MS, KS, NG, SY, TI, KM, MY, YY, K Nakagawa, and S-iW declare no competing interests. Dr. YS reports grants from Janssen and Japan Clinical Research Operations. KK reports personal fees from AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Chugai, Eli Lilly, and Ono outside the submitted work. Dr. YO reports grants from AbbVie, grants from Roche, and personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb Grants, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, and AstraZeneca. KK reports personal fees from Chugai, Eli Lilly, Ono Pharma Co. Ltd., Taiho, and Pfizer Taiho Pharma Co. Ltd., outside the submitted work. Dr. YO reports grants from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb Grants, Kyorin, and Preferred Network; and grants and personal fees from AZK, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Ono, Novartis, and Pfizer; and personal fees from AstraZeneca. KK reports personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Chugai, Guardant Health Inc., Illumina, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Taiho, and Thermo Fisher outside the submitted work. Dr. HH reports grants and personal fees from Chugai, Ono, and Roche; grants from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi-Sankyo, Genomic Health, Janssen, and Merck Biopharma, and personal fees from AstraZeneca. KK reports personal fees from Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Eli Lilly, and Kyowa-Kirin, outside the submitted work. Dr. K Naoki reports personal fees from AstraZeneca, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim outside the submitted work. Dr. TT reports grants from Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, and Foundation for Promotion Cancer Research Grant for Medical Research, and personal fees from Nippon Medical School Foundation, outside the submitted work. Dr. RH reports grants from JST AIP-PRISM (Grant Number JPMJCR18Y4), from null, outside the submitted work. Dr. Yamamoto reports grants from Chugai, Taiho, Eisai, Lilly, Quintiles, Astellas, BMS, Novartis, Daiichi-Sankyo, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Kyowa-Hakko Kirin, Bayer, ONO PHARMACEUTICAL CO., LTD, and Takeda; and personal fees from ONO PHARMACEUTICAL CO., LTD, Chugai, Eisai, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Cmic; and grants from Janssen Pharma, MSD, Merck, GSK, Sumitomo Dainippon, Chiome Bioscience Inc., Otsuka, Carna Biosciences, Genmab, TORAY, KAKEN, Shionogi, AstraZeneca, and Cmic; and personal fees from Eisai, Daiichi-Sankyo, MERCK, and Healios, outside the submitted work. Dr. RH reports grants from NEC and Ono, and personal fees from AstraZeneca, Chugai, MSD, Novartis, Roche, Daiichi-Sankyo, Takeda, Eli Lilly, and Janssen, outside the submitted work. Dr. TK reports grants from AMED, outside the submitted work. Dr. YO reports grants from Taiho, Eli Lilly, Kyorin, Daiichi-Sankyo, Dainippon-Sumitomo, Janssen, Kissei, LOXO, Novartis, and Takeda, and personal fees from AstraZeneca. KK reports personal fees from Amgen, AnHeeart Therapeutics Inc., Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celltrion, Chugai, Kyowa-Hakko Kirin, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Nippon Kayaku, Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Pfizer, Taiho, and Eli Lilly, outside the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- Paz-Ares L, Dvorkin M, Chen Y, Reinmuth N, Hotta K, Trukhin D, et al. Durvalumab plus platinum–etoposide versus platinum–etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2019;394:1929–39. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32222-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Morgensztern D, Besse B, Greillier L, Santana-Davila R, Ready N, Hann CL, et al. Efficacy and safety of rovalpituzumab tesirine in third-line and beyond patients with DLL3-expressing, relapsed/refractory small-cell lung cancer: results from the phase II TRINITY study. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25:6958–66. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-19-1133. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

