Systemic Ropivacaine Concentrations Following Local Infiltration Analgesia and Femoral Nerve Block in Older Patients Undergoing Total Knee Arthroplasty
- PMID: 37731601
- PMCID: PMC10508276
- DOI: 10.2147/LRA.S425353
Systemic Ropivacaine Concentrations Following Local Infiltration Analgesia and Femoral Nerve Block in Older Patients Undergoing Total Knee Arthroplasty
Abstract
Purpose: The study examined the pharmacokinetic profile of fixed formulation mixtures comprising 225 mg of ropivacaine for local infiltration analgesia with or without epinephrine, and femoral nerve block in older patients presenting for orthopedic surgery and explored potential influences of block type, age, and body weight on this profile.
Patients and methods: Twenty four patients scheduled for total knee arthroplasty were randomly assigned to three groups: femoral nerve block, local infiltration analgesia with epinephrine and local infiltration analgesia without epinephrine. Blood samples were collected at 10, 30, 60, and 120 min following the block and total plasma concentrations of ropivacaine were quantified by high performance liquid chromatography.
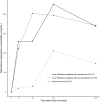
Results: The mean individual peak total plasma concentrations of ropivacaine in local infiltration analgesia with and without epinephrine, and femoral nerve block group were 0.334, 0.490 and 0.545 μg mL-1 (p = 0.16). Local infiltration with epinephrine group had significantly lower plasma ropivacaine concentrations at 30, 60 and 120 minutes. The plasma ropivacaine concentrations exceeded 2.2 μg mL-1 in one patient. Age, but not body weight, had a moderate correlation with peak plasma ropivacaine concentration (r = 0.37, p = 0.08).
Conclusion: Administration of a fixed 225 mg dose of ropivacaine for local infiltration analgesia with epinephrine and femoral nerve block results in plasma ropivacaine concentrations below the toxicity threshold, indicating their safety. The use of local infiltration analgesia with epinephrine provides a greater safety margin, as local infiltration analgesia without epinephrine may lead to ropivacaine concentrations associated with symptoms of local anesthetic toxicity.
Keywords: anesthetic techniques; anesthetics local; arthroplasty; local anesthetics; regional; ropivacaine; toxicity.
© 2023 Kazune et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

