Clinical outcomes of ramucirumab plus docetaxel in the treatment of patients with non-small cell lung cancer after immunotherapy: a systematic literature review
- PMID: 37731641
- PMCID: PMC10507469
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1247879
Clinical outcomes of ramucirumab plus docetaxel in the treatment of patients with non-small cell lung cancer after immunotherapy: a systematic literature review
Abstract
Introduction: In the REVEL trial, ramucirumab plus docetaxel demonstrated significant improvements in overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall response rate (ORR) compared with placebo plus docetaxel for treatment of metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that progressed during or after platinum-based chemotherapy. Since the approval of ramucirumab plus docetaxel, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), either as single agents or in combination with chemotherapy, have become the standard of care for first-line treatment of patients with advanced NSCLC. However, efficacy and safety data for ramucirumab plus docetaxel after prior ICI treatment from randomized controlled clinical studies are lacking.
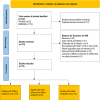
Methods: Following Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines, a systematic literature review was performed. Electronic databases and select international oncology conference proceedings were searched. Studies published between 01 January 2014 and 01 July 2022, which evaluated 2 efficacy outcomes (and included at least 1 time-to-event endpoint) or safety outcomes of ramucirumab plus docetaxel in NSCLC that progressed after prior ICI treatment, were identified. Twelve studies were included in the analysis. Two treatment groups were selected: ramucirumab plus docetaxel after prior ICI ± chemotherapy (RAM + DTX ICI pre-treated) and ramucirumab plus docetaxel after prior chemotherapy only (RAM + DTX ICI naïve). OS, PFS, ORR, disease control rate (DCR), and safety data were extracted and descriptively summarized across both treatment groups.
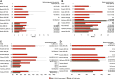
Results: The pooled weighted median PFS and median OS were 5.7 months (95% confidence interval [CI]: 3.9-6.8) and 11.2 months (95% CI: 7.5-17.5), respectively, in the RAM + DTX ICI pre-treated group and 3.8 months (95% CI: 2.3-4.1) and 13.5 months (95% CI: 8-24.0), respectively, in the RAM + DTX ICI naïve group. The ORR and DCR ranged from 20.9% to 60.0% and from 62.4% to 90.0%, respectively, in the RAM + DTX ICI pre-treated group and from 17.7% to 20.0% and from 57.1% to 75.0%, respectively, in the RAM + DTX ICI naïve group. The safety profile across studies was consistent between both treatment groups, and no new safety signals were reported.
Conclusions: Cumulatively, these results support the combination of ramucirumab plus docetaxel as an effective and safe subsequent therapy for the treatment of patients with metastatic NSCLC with disease progression irrespective of previous ICI treatment.
Keywords: antiangiogenic therapy; docetaxel; immune checkpoint inhibitors; non-small cell lung cancer; ramucirumab.
Copyright © 2023 Garon, Visseren-Grul, Rizzo, Puri, Chenji and Reck.
Conflict of interest statement
Author EG is a consultant and/or Advisor for AbbVie, ABL Bio, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Dracen Pharmaceutical, EMD Serono Inc, Eisai Co Ltd, Eli Lilly and Company, Gilead Sciences Inc, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck & Co, Natera, Novartis, Personalis, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, Shionogi Inc, Xilio Therapeutics, and Zymeworks. He also reports Grants/Research Support from ABL Bio, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Dynavax Technologies, Eli Lilly and Company, EMD Serono Inc, Genentech, Gilead Sciences Inc, Iovance Biotherapeutics, Merck, Mirati Therapeutics, Neon Therapeutics and Novartis. He also reports sponsored Independent Medical Education from Daiichi Sankyo and Ipsen and travel from A2 Bio and Novartis. Authors CV-G, MTR, TP, and SC are all employees of Eli Lilly and Company with stock options. Author MR receives consulting fees, payment or honoraria, and support for attending meetings/travel from Amgen, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly and Company, Merck & Co, MSD, Mirati Therapeutics, Novartis, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, and Roche. He is also on the advisory board or data safety monitoring board of Daiichi Sankyo and Sanofi.The authors declare that this study was funded by Eli Lilly and Company. Eli Lilly and Company had the following involvement in the study: data collection, data analysis, data interpretation, writing of the article, and decision to submit it for publication in collaboration with the authors.
Figures

References
-
- Gadgeel S, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Speranza G, Esteban E, Felip E, Dómine M, et al. Updated analysis from KEYNOTE-189: pembrolizumab or placebo plus pemetrexed and platinum for previously untreated metastatic nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol (2020) 38(14):1505–17. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.03136 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Socinski MA, Nishio M, Jotte RM, Cappuzzo F, Orlandi F, Stroyakovskiy D, et al. IMpower150 final overall survival analyses for atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and chemotherapy in first-line metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol (2021) 16(11):1909–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2021.07.009 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Paz-Ares L, Ciuleanu T-E, Cobo M, Schenker M, Zurawski B, Menezes J, et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab combined with two cycles of chemotherapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 9LA): an international, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol (2021) 22(2):198–211. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30641-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Johnson ML, Cho BC, Luft A, Alatorre-Alexander J, Geater SL, Laktionov K, et al. Durvalumab with or without tremelimumab in combination with chemotherapy as first-line therapy for metastatic non–small-cell lung cancer: the phase III POSEIDON study. J Clin Oncol (2023) 41(6):1213–27. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.00975 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

