This is a preprint.
Human Learning of Hierarchical Graphs
- PMID: 37731654
- PMCID: PMC10508785
Human Learning of Hierarchical Graphs
Update in
-
Human learning of hierarchical graphs.Phys Rev E. 2024 Apr;109(4-1):044305. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.109.044305. Phys Rev E. 2024. PMID: 38755869
Abstract
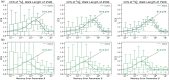
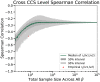
Humans are constantly exposed to sequences of events in the environment. Those sequences frequently evince statistical regularities, such as the probabilities with which one event transitions to another. Collectively, inter-event transition probabilities can be modeled as a graph or network. Many real-world networks are organized hierarchically and understanding how these networks are learned by humans is an ongoing aim of current investigations. While much is known about how humans learn basic transition graph topology, whether and to what degree humans can learn hierarchical structures in such graphs remains unknown. Here, we investigate how humans learn hierarchical graphs of the Sierpiński family using computer simulations and behavioral laboratory experiments. We probe the mental estimates of transition probabilities via the surprisal effect: a phenomenon in which humans react more slowly to less expected transitions, such as those between communities or modules in the network. Using mean-field predictions and numerical simulations, we show that surprisal effects are stronger for finer-level than coarser-level hierarchical transitions. Notably, surprisal effects at coarser levels of the hierarchy are difficult to detect for limited learning times or in small samples. Using a serial response experiment with human participants (n=100), we replicate our predictions by detecting a surprisal effect at the finer-level of the hierarchy but not at the coarser-level of the hierarchy. To further explain our findings, we evaluate the presence of a trade-off in learning, whereby humans who learned the finer-level of the hierarchy better tended to learn the coarser-level worse, and vice versa. Taken together, our computational and experimental studies elucidate the processes by which humans learn sequential events in hierarchical contexts. More broadly, our work charts a road map for future investigation of the neural underpinnings and behavioral manifestations of graph learning.
Figures
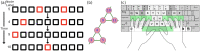
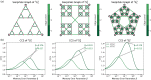

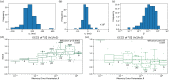
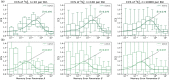

References
-
- Saffran J. R., Aslin R. N., and Newport E. L., Statistical learning by 8-month-old infants, Science 274, 1926 - PubMed
-
- Fiser J. and Aslin R. N., Statistical learning of higher-order temporal structure from visual shape sequences, Journal of experimental psychology. Learning, memory, and cognition 28, 458 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Kidd E., Arciuli J., Christiansen M. H., Isbilen E. S., Revius K., and Smithson M., Measuring children’s auditory statistical learning via serial recall, Journal of experimental child psychology 200, 104964 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Pudhiyidath A., Morton N. W., Duran R. V., Schapiro A. C., Momennejad I., Hinojosa-Rowland D. M., Molitor R. J., and Preston A. R., Representations of temporal community structure in hippocampus and precuneus predict inductive reasoning decisions, Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience , 1 (2022), https://direct.mit.edu/jocn/articlepdf/doi/10.1162/jocna01864/2023013/jo.... - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
