This is a preprint.
Evaluation of large language models for discovery of gene set function
- PMID: 37731657
- PMCID: PMC10508824
Evaluation of large language models for discovery of gene set function
Update in
-
Evaluation of large language models for discovery of gene set function.Nat Methods. 2025 Jan;22(1):82-91. doi: 10.1038/s41592-024-02525-x. Epub 2024 Nov 28. Nat Methods. 2025. PMID: 39609565 Free PMC article.
Abstract
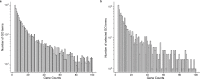
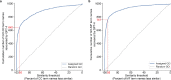
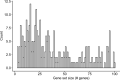
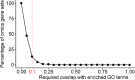
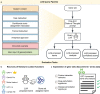
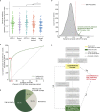
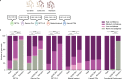
Gene set analysis is a mainstay of functional genomics, but it relies on curated databases of gene functions that are incomplete. Here we evaluate five Large Language Models (LLMs) for their ability to discover the common biological functions represented by a gene set, substantiated by supporting rationale, citations and a confidence assessment. Benchmarking against canonical gene sets from the Gene Ontology, GPT-4 confidently recovered the curated name or a more general concept (73% of cases), while benchmarking against random gene sets correctly yielded zero confidence. Gemini-Pro and Mixtral-Instruct showed ability in naming but were falsely confident for random sets, whereas Llama2-70b had poor performance overall. In gene sets derived from 'omics data, GPT-4 identified novel functions not reported by classical functional enrichment (32% of cases), which independent review indicated were largely verifiable and not hallucinations. The ability to rapidly synthesize common gene functions positions LLMs as valuable 'omics assistants.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Declarations TI is a co-founder, member of the advisory board, and has an equity interest in Data4Cure and Serinus Biosciences. TI is a consultant for and has an equity interest in Ideaya Biosciences. The terms of these arrangements have been reviewed and approved by the University of California San Diego in accordance with its conflict-of-interest policies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of large language models for discovery of gene set function.Nat Methods. 2025 Jan;22(1):82-91. doi: 10.1038/s41592-024-02525-x. Epub 2024 Nov 28. Nat Methods. 2025. PMID: 39609565 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of large language models for discovery of gene set function.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Sep 18:rs.3.rs-3270331. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3270331/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Nat Methods. 2025 Jan;22(1):82-91. doi: 10.1038/s41592-024-02525-x. PMID: 37790547 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
A dataset and benchmark for hospital course summarization with adapted large language models.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2025 Mar 1;32(3):470-479. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocae312. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2025. PMID: 39786555
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beissbarth T. & Speed T. P. GOstat: find statistically overrepresented Gene Ontologies within a group of genes. Bioinformatics 20, 1464–1465 (2004). - PubMed
