Effects of WeChat platform-based continuing care on self-management and quality of life in patients with arthritis: A quasi-experimental study
- PMID: 37732135
- PMCID: PMC10508053
- DOI: 10.1177/20552076231197104
Effects of WeChat platform-based continuing care on self-management and quality of life in patients with arthritis: A quasi-experimental study
Abstract
Objective: To assess the effects of WeChat platform-based continuing care for arthritis on patients' self-management, self-efficiency, quality of life (QoL), and medication compliance.
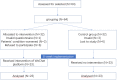
Methods: A study was conducted on arthritis patients recruited between December 2017 and February 2018 and divided into two groups. The intervention group received continuing care from the WeChat platform and regular follow-ups, while the control group only received regular follow-ups. The outcomes in both groups were assessed using questionnaires twice: before the study (T0) and eight weeks after T0 (T1), which consists of the evaluation of self-management, QoL, self-efficacy, and medication compliance.
Results: There were 23 people in each of the intervention and control groups completed two outcome measures. At eight weeks, participants in the intervention group showed an improvement in psychological QoL, cognitive symptom management, and self-efficacy, compared to the control group (QoL scores: mean difference in change between groups was 12.29, 95% CI: 4.51, 20.07, p < 0.001; cognitive symptom management: mean difference in change between groups was 0.65, 95% CI: 0.24, 1.05, p < 0.001; self-efficacy: mean difference in change between groups was 0.69, 95% CI: 0.14, 1.24, p < 0.05). Self-management, self-efficacy, and psychological quality of life were significantly improved in the intervention group before and after the intervention (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Using the WeChat platform for continuing care is useful in improving the psychological state, self-efficacy, and self-management ability of patients with arthritis. The study is relevant to Clinical Practice.
Keywords: Continuing care; WeChat; arthritis; medication compliance; quality of life; self-efficacy; self-management.
© The Author(s) 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of WeChat platform-based health management on health and self-management effectiveness of patients with severe chronic heart failure.World J Clin Cases. 2021 Dec 6;9(34):10576-10584. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i34.10576. World J Clin Cases. 2021. PMID: 35004989 Free PMC article.
-
Web-Based TangPlan and WeChat Combination to Support Self-management for Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: Randomized Controlled Trial.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2022 Mar 30;10(3):e30571. doi: 10.2196/30571. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2022. PMID: 35353055 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of probiotics supplementation combined with WeChat platform health management on nutritional status, inflammatory factors, and quality of life in patients with mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis: a randomized trial.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Jun;10(6):6606-6616. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-1056. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 34154363 Clinical Trial.
-
Self-management among type 2 diabetes patients via the WeChat application: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2021 Feb;46(1):4-16. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13264. Epub 2020 Oct 21. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2021. PMID: 33085789
-
Psychological interventions for people with hemophilia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Mar 18;3(3):CD010215. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010215.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32187661 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Study on the impact of WeChat platform continuity care on complications and self-care ability in colostomy patients.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jul 11;104(28):e43175. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043175. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40660592 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of WeChat-based telehealth on patients reported outcomes of hypertension: a randomized controlled trial.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):22035. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-04504-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40596064 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Influence of exercise prescription intervention based on WeChat on glycolipid metabolism and fitness of suboptimal-health teachers.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 May 24;103(21):e38167. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038167. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38788028 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Johnsson PM, Eberhardt K. Hand deformities are important signs of disease severity in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2009; 48: 1398–1401. - PubMed
-
- Lubar D, White PH, Callahan LF, et al. A national public health agenda for osteoarthritis 2010. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2010; 39: 323–326. - PubMed
-
- Khanna R, Smith MJ. Utilization and costs of medical services and prescription medications for rheumatoid arthritis among recipients covered by a state Medicaid program: a retrospective, cross-sectional, descriptive, database analysis. Clin Ther 2007; 29: 2456–2467. - PubMed
-
- Akhter E, Bilal S, Kiani A, et al. Prevalence of arthritis in India and Pakistan: a review. Rheumatol Int. 2011; 31: 849–855. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources