TGF-β pathways in aging and immunity: lessons from Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 37732316
- PMCID: PMC10507863
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1220068
TGF-β pathways in aging and immunity: lessons from Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
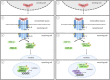
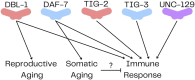
The Transforming Growth Factor-β (TGF-β) superfamily of signaling molecules plays critical roles in development, differentiation, homeostasis, and disease. Due to the conservation of these ligands and their signaling pathways, genetic studies in invertebrate systems including the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans have been instrumental in identifying signaling mechanisms. C. elegans is also a premier organism for research in longevity and healthy aging. Here we summarize current knowledge on the roles of TGF-β signaling in aging and immunity.
Keywords: BMP; C. elegans; TGF-β; aging; innate immunity.
Copyright © 2023 Yamamoto and Savage-Dunn.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

