The effect of dispersal on asymptotic total population size in discrete- and continuous-time two-patch models
- PMID: 37733146
- PMCID: PMC10514157
- DOI: 10.1007/s00285-023-01984-8
The effect of dispersal on asymptotic total population size in discrete- and continuous-time two-patch models
Abstract
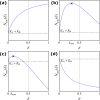
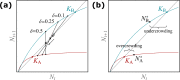
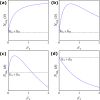
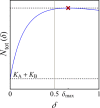
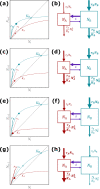
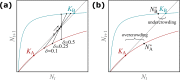
Many populations occupy spatially fragmented landscapes. How dispersal affects the asymptotic total population size is a key question for conservation management and the design of ecological corridors. Here, we provide a comprehensive overview of two-patch models with symmetric dispersal and two standard density-dependent population growth functions, one in discrete and one in continuous time. A complete analysis of the discrete-time model reveals four response scenarios of the asymptotic total population size to increasing dispersal rate: (1) monotonically beneficial, (2) unimodally beneficial, (3) beneficial turning detrimental, and (4) monotonically detrimental. The same response scenarios exist for the continuous-time model, and we show that the parameter conditions are analogous between the discrete- and continuous-time setting. A detailed biological interpretation offers insight into the mechanisms underlying the response scenarios that thus improve our general understanding how potential conservation efforts affect population size.
Keywords: Dispersal; Population dynamics; Spatial fragmentation; Total population size; Two-patch model.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Connectivity, conservation and catch: Understanding the effects of dispersal between harvested and protected patches.Theor Popul Biol. 2025 Jun;163:91-105. doi: 10.1016/j.tpb.2025.03.005. Epub 2025 Mar 24. Theor Popul Biol. 2025. PMID: 40139277
-
One way or another: Combined effect of dispersal and asymmetry on total realized asymptotic population abundance.Math Biosci. 2024 Jul;373:109206. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2024.109206. Epub 2024 May 8. Math Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38729519
-
New insights into the combined effect of dispersal and local dynamics in a two-patch population model.J Theor Biol. 2024 Dec 7;595:111942. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2024.111942. Epub 2024 Sep 17. J Theor Biol. 2024. PMID: 39299679
-
Is dispersal always beneficial to carrying capacity? New insights from the multi-patch logistic equation.Theor Popul Biol. 2015 Dec;106:45-59. doi: 10.1016/j.tpb.2015.10.001. Epub 2015 Oct 16. Theor Popul Biol. 2015. PMID: 26472064
-
Causes and consequences of animal dispersal strategies: relating individual behaviour to spatial dynamics.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2005 May;80(2):205-25. doi: 10.1017/s1464793104006645. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2005. PMID: 15921049 Review.
References
-
- Adler FR. Migration alone can produce persistence of host-parasitoid models. Am Nat. 1993;141:642–650. doi: 10.1086/285496. - DOI
-
- Allen LJS, Bolker BM, Lou Y, et al. Asymptotic profiles of the steady states for an SIS epidemic patch model. SIAM J Appl Math. 2007;67:1283–1309. doi: 10.1137/060672522. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

