Mitigation of trauma-induced endotheliopathy by activated protein C: A potential therapeutic for postinjury thromboinflammation
- PMID: 37733304
- PMCID: PMC10841096
- DOI: 10.1097/TA.0000000000004142
Mitigation of trauma-induced endotheliopathy by activated protein C: A potential therapeutic for postinjury thromboinflammation
Abstract
Background: Activated Protein C (aPC) plays dual roles after injury, driving both trauma-induced coagulopathy (TIC) by cleaving, and thus inactivating, factors Va and VIIIa and depressing fibrinolysis while also mediating an inflammomodulatory milieu via protease activated receptor-1 (PAR-1) cytoprotective signaling. Because of this dual role, it represents and ideal target for study and therapeutics after trauma. A known aPC variant, 3K3A-aPC, has been engineered to preserve cytoprotective activity while retaining minimal anticoagulant activity rendering it potentially ideal as a cytoprotective therapeutic after trauma. We hypothesized that 3K3A-aPC would mitigate the endotheliopathy of trauma by protecting against endothelial permeability.
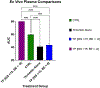
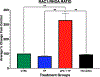
Methods: We used electric cell-substrate impedance sensing to measure permeability changes in real time in primary endothelial cells. These were cultured, grown to confluence, and treated with a 2 μg/mL solution of 3K3A-aPC at 180 minutes, 120 minutes, 60 minutes, 30 minutes prior to stimulation with ex vivo plasma taken from severely injured trauma patients (Injury Severity Score > 15 and BD < -6) (trauma plasma [TP]). Cells treated with thrombin and untreated cells were included in this study as control groups. Permeability changes were recorded in real time via electric cell-substrate impedance sensing for 30 minutes after treatment with TP. We quantified permeability changes in the control and treatment groups as area under the curve (AUC). Rac1/RhoA activity was also compared between these groups. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA followed by a post hoc analysis using Tukey's multiple comparison's test.
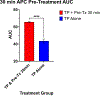
Results: Treatment with aPC mitigated endothelial permeability induced by ex vivo trauma plasma at all pre-treatment time points. The AUC of the 30-minute 3K3A-aPC pretreatment group was higher than TP alone (mean diff. 22.12 95% CI [13.75, 30.49], p < 0.0001) (Figure). Moreover, the AUC of the 60-minute, 120-minute, and 180-minute pretreatment groups was also higher than TP alone (mean diff., 16.30; 95% confidence interval [CI], 7.93-24.67; 19.43; 95% CI, 11.06-27.80, and 18.65; 95% CI, 10.28-27.02;, all p < 0.0001, respectively). Rac1/RhoA activity was higher in the aPC pretreatment group when compared with all other groups ( p < 0.01).
Conclusion: Pretreatment with 3K3A-aPC, which retains its cytoprotective function but has only ~5% of its anticoagulant function, abrogates the effects of trauma-induced endotheliopathy. This represents a potential therapeutic treatment for dysregulated thromboinflammation for injured patients by minimizing aPC's role in trauma-induced coagulopathy while concurrently amplifying its essential cytoprotective function.
Level of evidence: Prognostic and Epidemiological; Level III.
Copyright © 2023 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

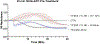
References
-
- Cohen MJ, Bir N, Rahn P, Dotson R, Brohi K, Chesebro BB, et al. Protein C depletion early after trauma increases the risk of ventilator-associated pneumonia. J Trauma. 2009;67(6):1176–81. - PubMed
-
- Mosnier LO, Zlokovic BV, Griffin JH. The cytoprotective protein C pathway. Blood. 2007;109(8):3161–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

