Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy vs No Axillary Surgery in Patients With Small Breast Cancer and Negative Results on Ultrasonography of Axillary Lymph Nodes: The SOUND Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 37733364
- PMCID: PMC10514873
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2023.3759
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy vs No Axillary Surgery in Patients With Small Breast Cancer and Negative Results on Ultrasonography of Axillary Lymph Nodes: The SOUND Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: Sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) is the standard of care for axillary node staging of patients with early breast cancer (BC), but its necessity can be questioned since surgery for examination of axillary nodes is not performed with curative intent.
Objective: To determine whether the omission of axillary surgery is noninferior to SLNB in patients with small BC and a negative result on preoperative axillary lymph node ultrasonography.
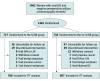
Design, setting, and participants: The SOUND (Sentinel Node vs Observation After Axillary Ultra-Sound) trial was a prospective noninferiority phase 3 randomized clinical trial conducted in Italy, Switzerland, Spain, and Chile. A total of 1463 women of any age with BC up to 2 cm and a negative preoperative axillary ultrasonography result were enrolled and randomized between February 6, 2012, and June 30, 2017. Of those, 1405 were included in the intention-to-treat analysis. Data were analyzed from October 10, 2022, to January 13, 2023.
Intervention: Eligible patients were randomized on a 1:1 ratio to receive SLNB (SLNB group) or no axillary surgery (no axillary surgery group).
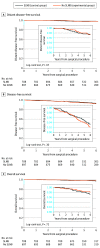
Main outcomes and measures: The primary end point of the study was distant disease-free survival (DDFS) at 5 years, analyzed as intention to treat. Secondary end points were the cumulative incidence of distant recurrences, the cumulative incidence of axillary recurrences, DFS, overall survival (OS), and the adjuvant treatment recommendations.
Results: Among 1405 women (median [IQR] age, 60 [52-68] years) included in the intention-to-treat analysis, 708 were randomized to the SLNB group, and 697 were randomized to the no axillary surgery group. Overall, the median (IQR) tumor size was 1.1 (0.8-1.5) cm, and 1234 patients (87.8%) had estrogen receptor-positive ERBB2 (formerly HER2 or HER2/neu), nonoverexpressing BC. In the SLNB group, 97 patients (13.7%) had positive axillary nodes. The median (IQR) follow-up for disease assessment was 5.7 (5.0-6.8) years in the SLNB group and 5.7 (5.0-6.6) years in the no axillary surgery group. Five-year distant DDFS was 97.7% in the SLNB group and 98.0% in the no axillary surgery group (log-rank P = .67; hazard ratio, 0.84; 90% CI, 0.45-1.54; noninferiority P = .02). A total of 12 (1.7%) locoregional relapses, 13 (1.8%) distant metastases, and 21 (3.0%) deaths were observed in the SLNB group, and 11 (1.6%) locoregional relapses, 14 (2.0%) distant metastases, and 18 (2.6%) deaths were observed in the no axillary surgery group.
Conclusions and relevance: In this randomized clinical trial, omission of axillary surgery was noninferior to SLNB in patients with small BC and a negative result on ultrasonography of the axillary lymph nodes. These results suggest that patients with these features can be safely spared any axillary surgery whenever the lack of pathological information does not affect the postoperative treatment plan.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02167490.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Sentinel Node Biopsy for Early Breast Cancer-A SOUND for De-escalation.JAMA Oncol. 2023 Nov 1;9(11):1501-1503. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2023.3667. JAMA Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37733358 No abstract available.
-
The SOUND Randomized Clinical Trial Results.JAMA Oncol. 2024 May 1;10(5):676-677. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2024.0128. JAMA Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38512288 No abstract available.
-
The SOUND Randomized Clinical Trial Results.JAMA Oncol. 2024 May 1;10(5):675-676. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2024.0122. JAMA Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38512291 No abstract available.
-
The SOUND Randomized Clinical Trial Results.JAMA Oncol. 2024 May 1;10(5):676. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2024.0125. JAMA Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38512296 No abstract available.
References
-
- Krag DN, Anderson SJ, Julian TB, et al. . Sentinel-lymph-node resection compared with conventional axillary-lymph-node dissection in clinically node-negative patients with breast cancer: overall survival findings from the NSABP B-32 randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(10):927-933. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70207-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Giuliano AE, Ballman KV, McCall L, et al. . Effect of axillary dissection vs no axillary dissection on 10-year overall survival among women with invasive breast cancer and sentinel node metastasis: the ACOSOG Z0011 (Alliance) randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;318(10):918-926. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.11470 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Galimberti V, Cole BF, Viale G, et al. ; International Breast Cancer Study Group Trial 23-01 . Axillary dissection versus no axillary dissection in patients with breast cancer and sentinel-node micrometastases (IBCSG 23-01): 10-year follow-up of a randomised, controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19(10):1385-1393. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30380-2 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

