Patient-reported Primary Care Video and Telephone Telemedicine Preference Shifts During the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 37733433
- PMCID: PMC10592113
- DOI: 10.1097/MLR.0000000000001916
Patient-reported Primary Care Video and Telephone Telemedicine Preference Shifts During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
Background: Patient perceptions of primary care telephone and video telemedicine and whether COVID-19 pandemic-related telemedicine exposure shifted patients' visit preference is unknown.
Objectives: We examined patient surveys to understand the health care experience of patients seeking primary care through telemedicine and how patients expected their preferences to shift as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Research design/subjects: In an integrated delivery system that shifted to a "telemedicine-first" health care model during the COVID-19 pandemic, we sampled monthly and collected 1000 surveys from adults with primary care telemedicine visits scheduled through the online patient portal between 3/16/2020 and 10/31/2020.
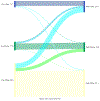
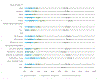
Measures: Participants reported their preferred primary care visit modality (telephone, video, or in-person visits) across 3 time points: before, during and (hypothetically) after the COVID-19 pandemic, and reported their general assessment of primary care visits during the pandemic.
Results: The majority of participants preferred in-person visits before (69%) and after the COVID-19 pandemic (57%). However, most participants reported a preference for telemedicine visits during the pandemic and continue to prefer telemedicine visits at a 12% higher rate post-pandemic. Many participants (63%) expressed interest in using telemedicine at least some of the time. Among participants reporting a recent telemedicine visit, 85% agreed that the visit addressed their health needs.
Conclusion: As primary care visit modality preferences continue to evolve, patients anticipate that they will continue to prefer telemedicine visits, both video and telephone, at an increased rate than before the COVID-19 pandemic.
Copyright © 2023 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chang JE, Lindenfeld Z, Albert SL, et al. , Telephone vs. Video Visits During COVID-19: Safety-Net Provider Perspectives. J Am Board Fam Med, 2021. 34(6): p. 1103–1114. - PubMed
-
- Friedman AB, Gervasi S, Song H, et al. , Telemedicine catches on: changes in the utilization of telemedicine services during the COVID-19 pandemic. Am J Manag Care, 2022. 28(1): p. e1–e6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

