Nicotine flux as a powerful tool for regulating nicotine delivery from e-cigarettes: Protocol of two complimentary randomized crossover clinical trials
- PMID: 37733666
- PMCID: PMC10513228
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291786
Nicotine flux as a powerful tool for regulating nicotine delivery from e-cigarettes: Protocol of two complimentary randomized crossover clinical trials
Abstract
Introduction: Electronic cigarette (EC) use has increased rapidly in the last decade, especially among youth. Regulating nicotine delivery from ECs could help curb youth uptake and leverage EC use in harm reduction yet is complicated by varying device and liquid variables that affect nicotine delivery. Nicotine flux, the nicotine emission rate, is a parameter that incorporates these variables and focuses on the performance rather than the design of an EC. Nicotine flux therefore could be a powerful regulatory tool if it is shown empirically to predict nicotine delivery and subjective effects related to dependence.
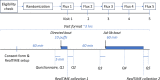
Methods and analysis: This project consists of two complementary clinical trials. In Trial I, we will examine the relationship between nicotine flux and the rate and dose of nicotine delivery from ECs, hence, impacting abuse liability. It will also examine the extent to which this relationship is mediated by nicotine form (i.e., freebase versus protonated). At Yale School of Medicine (YSM), study participants will puff EC devices under conditions that differ by flux and form, while arterial blood is sampled in high time resolution. In Trial II, we will assess the relationship between nicotine flux, form, and subjective effects. At the American University of Beirut (AUB), participants will use EC devices with varying nicotine fluxes and forms, while dependency measures, such as the urge to use ECs, nicotine craving, and withdrawal symptoms, will be assessed. We will also monitor puffing intensity and real-time exposure to toxicants.
Ethics and dissemination: The protocol of Trial I and Trial II was approved by YSM and AUB IRBs, respectively. We will disseminate study results through peer-reviewed publications and conference presentations.
Trial registration: NCT05706701 for Trial I and NCT05430334 for Trial II.
Copyright: © 2023 El-Hellani et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
AS and TEissenberg are paid consultants in litigation against the tobacco and EC industry and are named on a patent for a device that measures the puffing behavior of EC users and another patent application for a smoking cessation intervention. TEissenberg is also named on a patent application for a smartphone app that determines EC device and liquid characteristics. All other authors declare no conflict of interest. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures



References
-
- WHO. WHO report on the global tobacco epidemic 2021: addressing new and emerging products. Geneva; 2021. Contract No.: Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

