Changes in the estimated glomerular filtration rate and predictors of the renal prognosis in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: A retrospective study during the 12 months after the initiation of tofogliflozin
- PMID: 37733761
- PMCID: PMC10513294
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0292014
Changes in the estimated glomerular filtration rate and predictors of the renal prognosis in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: A retrospective study during the 12 months after the initiation of tofogliflozin
Abstract
Background: The changes in the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and predictors of the renal prognosis were retrospectively assessed over the 12 months after the initiation of tofogliflozin, which has the shortest half-life among sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes and renal impairment.
Methods: In total, 158 patients treated with tofogliflozin between 2019 and 2021 were studied as the safety analysis set. One hundred and thirty subjects whose medication was continued over 12 months were investigated as the full analysis set. The subjects were divided into two groups based on the eGFR: normal- (eGFR ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m2, n = 87) and low- (eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2, n = 43) eGFR groups.
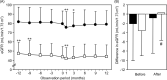
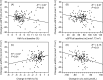
Results: The body weight, blood pressure, urinary protein excretion, and serum uric acid concentration decreased from baseline in both eGFR groups while the hemoglobin level increased. The eGFR did not significantly differ over time, except for the initial dip (-4.3±9.6 mL/min/1.73 m2 in the normal-eGFR group and -1.5±5.3 mL/min/1.73 m2 in the low-eGFR group). The change in the eGFR at 12 months after the initiation of tofogliflozin was -1.9±9.0 mL/min/1.73 m2 and 0.2±6.0 mL/min/1.73 m2 in the normal- and low-eGFR group, respectively. In the normal-eGFR group, the change in the eGFR showed a significant negative correlation with the HbA1c and eGFR at baseline, according to a multiple regression analysis. In the low-eGFR group, the change in the eGFR showed a significant negative correlation with urate-lowering agent use. The frequencies of adverse events specific for SGLT2 inhibitors were not significantly different between the normal- and low-eGFR groups.
Conclusions: Tofogliflozin may preserve renal function in the medium term in patients with type 2 diabetes and kidney impairment without an increase in specific adverse events.
Copyright: © 2023 Ito et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
H Ito has received funding support and lecture fees from Kowa Company, Ltd. and Taisho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and lecture fees from Eli Lilly Japan KK, Novo Nordisk Pharma Ltd., Sumitomo Pharma Co., Ltd., Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi KK, Daiichi Sankyo Company, Novartis Pharma KK, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Ltd., MSD KK, Astellas Pharma, Terumo Corporation, Mochida Pharmaceuticals, Teijin Pharma, Kissei Pharmaceuticals, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Sanwa Kagaku Kenkyusho, AstraZeneca KK, Kyowa Kirin Co. Ltd., Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Bayer Yakuhin, Ltd., EA Pharma Co., Ltd., Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Viatris Inc., and has received consulting fee from Becton, Dickinson and Company. H Inoue has received lecture fees from AstraZeneca KK. T Izutsu has received lecture fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk Pharma Ltd., Taisho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Kowa Company, Ltd. and Asahi Kasei Pharma Corporation. S Matsumoto has received lecture fees from Eli Lilly Japan KK, Novo Nordisk Pharma Ltd., Astellas Pharma, Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd. and AstraZeneca KK. S Antoku has received lecture fees from Kyowa Kirin Co. Ltd., Sanofi KK, Taisho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Company, and Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. T Yamasaki, T Mori and M Togane have no conflict of interest. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of Baseline Values of Renal Prognosis-related Factors on Their Changes after Initiating Tofogliflozin Treatment: A Retrospective Study in Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Renal Impairment.JMA J. 2024 Oct 15;7(4):571-579. doi: 10.31662/jmaj.2024-0128. Epub 2024 Sep 6. JMA J. 2024. PMID: 39513071 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Renal Function on the 52-Week Efficacy and Safety of the Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor Luseogliflozin in Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Clin Ther. 2016 Jan 1;38(1):66-88.e20. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.10.025. Epub 2015 Dec 22. Clin Ther. 2016. PMID: 26718606 Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor (tofogliflozin) on renal tubular damage in diabetic patients without albuminuria.Int Urol Nephrol. 2022 Aug;54(8):1907-1914. doi: 10.1007/s11255-021-03064-6. Epub 2021 Nov 29. Int Urol Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 34843041
-
SGLT2 inhibitors and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes with or without renal impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Prim Care Diabetes. 2018 Jun;12(3):265-283. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2018.02.001. Epub 2018 Feb 24. Prim Care Diabetes. 2018. PMID: 29482993
-
The Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes in Diabetic Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cardiorenal Med. 2020;10(1):1-10. doi: 10.1159/000503919. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Cardiorenal Med. 2020. PMID: 31743918
Cited by
-
Novel Therapeutics for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-A Look at the Past Decade and a Glimpse into the Future.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 21;12(7):1386. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071386. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39061960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Baseline Values of Renal Prognosis-related Factors on Their Changes after Initiating Tofogliflozin Treatment: A Retrospective Study in Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Renal Impairment.JMA J. 2024 Oct 15;7(4):571-579. doi: 10.31662/jmaj.2024-0128. Epub 2024 Sep 6. JMA J. 2024. PMID: 39513071 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, von Eynatten M, Mattheus M, et al.. Empaglifozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375: 323–34. - PubMed
-
- Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, de Zeeuw D, Fulcher G, Erondu N, at al. Canaglifozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377: 644–57. - PubMed
-
- Wiviott SD, Raz I, Bonaca MP, Mosenzon O, Kato ET, Cahn A, et al.. Dapaglifozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2019; 380: 347–57. - PubMed
-
- Bae JH, Park EG, Kim S, Kim SG, Hahn S, Kim NH. Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sci Rep. 2019; 9: 13009. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49525-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

