Long non-coding RNA as a potential diagnostic biomarker in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37733767
- PMCID: PMC10513217
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291921
Long non-coding RNA as a potential diagnostic biomarker in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is a group of malignancies arising from the epithelium of the head and neck. Despite efforts in treatment, results have remained unsatisfactory, and the death rate is high. Early diagnosis of HNSCC has clinical importance due to its high rates of invasion and metastasis. This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of lncRNAs in HNSCC patients.
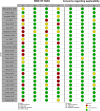
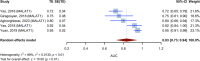
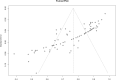
Methods: PubMed, ISI, SCOPUS, and EMBASE were searched for original publications published till April 2023 using MeSH terms and free keywords "long non-coding RNA" and "head and neck squamous cell carcinoma" and their expansions. The Reitsma bivariate random effect model pooled diagnostic test performance for studies that reported specificity and sensitivity; diagnostic AUC values from all trials were meta-analyzed using the random effects model with the inverse variance method.
Results: The initial database search yielded 3209 articles, and 25 studies met our criteria. The cumulative sensitivity and specificity for lncRNAs in the diagnosis of HNSCC were 0.74 (95%CI: 0.68-0.7 (and 0.79 (95%CI: 0.74-0.83), respectively. The pooled AUC value for all specimen types was found to be 0.83. Using the inverse variance method, 71 individual lncRNAs yielded a pooled AUC of 0.77 (95%CI: 0.74-0.79). Five studies reported on the diagnostic accuracy of the MALAT1 lncRNA with a pooled AUC value of 0.83 (95%CI: 0.73-0.94).
Conclusions: LncRNAs could be used as diagnostic biomarkers for HNSCC, but further investigation is needed to validate clinical efficacy and elucidate mechanisms. High-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics should be used to ascertain expression profiles.
Copyright: © 2023 Masrour et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Excavating novel diagnostic and prognostic long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: an integrated bioinformatics analysis of competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) and gene co-expression networks.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):12821-12838. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2003925. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34898376 Free PMC article.
-
Screening key lncRNAs with diagnostic and prognostic value for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma based on machine learning and mRNA-lncRNA co-expression network analysis.Cancer Biomark. 2020;27(2):195-206. doi: 10.3233/CBM-190694. Cancer Biomark. 2020. PMID: 31815689
-
Upregulation of the long non-coding RNA CASC9 as a biomarker for squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2019 Aug 14;19(1):806. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6021-6. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31412811 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Value of Salivary miRNA in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 29;22(13):7026. doi: 10.3390/ijms22137026. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34209954 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and function of long non-coding RNAs in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Exp Mol Pathol. 2020 Feb;112:104353. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2019.104353. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Exp Mol Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31812485 Review.
Cited by
-
Long non-coding RNA as potential diagnostic markers for acute myeloid leukemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Med. 2024 Jun;13(11):e7376. doi: 10.1002/cam4.7376. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38864480 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of circulating lncRNAs HOTAIR, ANRIL, and MEG3 in oral squamous cell carcinoma and their correlation with clinicopathological features.J Liq Biopsy. 2025 Jul 25;9:100315. doi: 10.1016/j.jlb.2025.100315. eCollection 2025 Sep. J Liq Biopsy. 2025. PMID: 40792230 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA MALAT1 as diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 29;19(10):e0308009. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308009. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39471147 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the expression pattern of ATXN1 and CDC42EP1 genes and related long noncoding RNAs in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Jul 13;51(1):796. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09719-8. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39002033
-
MicroRNA as a Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2025 Jan;8(1):e70070. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.70070. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2025. PMID: 39854617 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

