Structural basis for inactivation of PRC2 by G-quadruplex RNA
- PMID: 37733873
- PMCID: PMC11191771
- DOI: 10.1126/science.adh0059
Structural basis for inactivation of PRC2 by G-quadruplex RNA
Abstract
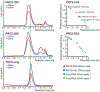
Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) silences genes through trimethylation of histone H3K27. PRC2 associates with numerous precursor messenger RNAs (pre-mRNAs) and long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) with a binding preference for G-quadruplex RNA. In this work, we present a 3.3-Å-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure of PRC2 bound to a G-quadruplex RNA. Notably, RNA mediates the dimerization of PRC2 by binding both protomers and inducing a protein interface composed of two copies of the catalytic subunit EZH2, thereby blocking nucleosome DNA interaction and histone H3 tail accessibility. Furthermore, an RNA-binding loop of EZH2 facilitates the handoff between RNA and DNA, another activity implicated in PRC2 regulation by RNA. We identified a gain-of-function mutation in this loop that activates PRC2 in zebrafish. Our results reveal mechanisms for RNA-mediated regulation of a chromatin-modifying enzyme.
Figures


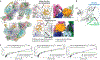

Update of
-
Structural basis for inactivation of PRC2 by G-quadruplex RNA.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 6:2023.02.06.527314. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.06.527314. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Science. 2023 Sep 22;381(6664):1331-1337. doi: 10.1126/science.adh0059. PMID: 36798278 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

