Effects of lactotripeptide ingestion and physical activity intervention on the fatigue status of middle-aged and older adults: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 37735182
- PMCID: PMC10514187
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-41669-2
Effects of lactotripeptide ingestion and physical activity intervention on the fatigue status of middle-aged and older adults: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
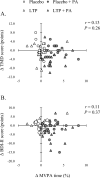
This randomized controlled trial aimed to investigate the effects of eight weeks of lactotripeptide (LTP) ingestion, physical activity (PA) intervention, and combined intervention on the fatigue status of middle-aged and older adults. A total of 78 middle-aged and older adults (63 ± 8 years of age) were randomly assigned to four groups: placebo, LTP, placebo with PA intervention (placebo + PA), and LTP with PA intervention (LTP + PA). All participants ingested the placebo or LTP tablets daily (three tablets/day). The placebo + PA and LTP + PA groups participated in a weekly supervised exercise class and were instructed to increase their moderate- to vigorous-intensity PA at home. The visual analog scale, Brief Fatigue Inventory, Profile of Mood States second edition (POMS2), and Beck Depression Inventory second edition (BDI-II) were administered before and after the intervention. No significant interactions or main effects were observed between LTP ingestion and PA intervention on any of the fatigue scales. The main-effect analyses revealed that the PA intervention improved the total mood disturbance score of the POMS2 (F = 5.22, P = 0.03) and BDI-II score (F = 4.81, P = 0.03). After the post hoc paired comparisons, the total mood disturbance and BDI-II scores improved more with the combined intervention than with the PA intervention alone (percentage difference between the effect of combined intervention and PA intervention alone was 3.7% for total mood disturbance score and 13.7% for BDI-II score). The present study suggests that eight weeks of LTP ingestion and PA intervention did not have a significant effect on fatigue status. However, the PA intervention improved mood status and depressive symptoms, and these effects were enhanced by LTP ingestion.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined effects of lactotripeptide and aerobic exercise on cognitive function and cerebral oxygenation in middle-aged and older adults.Am J Clin Nutr. 2019 Feb 1;109(2):353-360. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqy235. Am J Clin Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30624594 Clinical Trial.
-
Reduction of fatigue and anger-hostility by the oral administration of 5-aminolevulinic acid phosphate: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel study.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 29;10(1):16004. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72763-4. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32994490 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Lactotripeptide ingestion increases cerebral blood flow velocity in middle-aged and older adults.Nutr Res. 2018 May;53:61-66. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2018.03.009. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Nutr Res. 2018. PMID: 29703414 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of dried-bonito broth on mental fatigue and mental task performance in subjects with a high fatigue score.Physiol Behav. 2007 Dec 5;92(5):957-62. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2007.07.002. Epub 2007 Jul 25. Physiol Behav. 2007. PMID: 17655888 Clinical Trial.
-
Novel Augmentation Strategies in Major Depression.Dan Med J. 2017 Apr;64(4):B5338. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28385173 Review.
References
-
- Yancey JR, Thomas SM. Chronic fatigue syndrome: diagnosis and treatment. Am. Fam. Physician. 2012;86:741–746. - PubMed
-
- Latimer KM, Gunther A, Kopec M. Fatigue in adults: Evaluation and management. Am. Fam. Physician. 2023;108:58–69. - PubMed
-
- Japan Society of Fatigue Science. Guideline for Clinical Evaluation of Anti-fatigue Products and Services, 1–13 (2011).

