Ameliorative effects of aerobic training in girls with precocious puberty: role of leptin and ghrelin
- PMID: 37735188
- PMCID: PMC10575917
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-42828-1
Ameliorative effects of aerobic training in girls with precocious puberty: role of leptin and ghrelin
Abstract
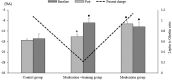
This study was an attempt to examine the changes in serum levels of ghrelin and leptin after 12-weeks of aerobic training and gonadotropin releasing hormone agonist (GnRH) treatment in girls with central precocious puberty. Thirty girls (6-8 years old) with precocious puberty who had received Triptorelin were randomly divided in two groups (medication and medication + training). Fifteen age-matched healthy girls (without precocious puberty) were also included as the control group. The medication + training group submitted an aerobic training program for 3 days/week with 20-75 min per day and 45-75% of maximum heart rate for 12-weeks. Serum levels of leptin, ghrelin, cholesterol, triglycerides and body mass index (BMI) were determined at baseline and 48 h after the last training session. The results indicated that leptin significantly decreased (p = 0.001) and ghrelin significantly increased (p = 0.001) in the medication + training group but no significant difference was observed in the ghrelin (p = 1) and leptin (p = 0.78) in the medication group. Leptin to ghrelin ratio indicated a decrease in medicine + training group (p = 0.028). Ghrelin were negatively correlated with leptin and BMI. The data indicated that aerobic training increased ghrelin and reduced leptin and leptin to ghrelin ratio but GnRH agonist treatment had no effect on plasma leptin and ghrelin levels.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Benefits of aerobic training in girls with precocious puberty: involvement of CRP and cortisol.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Sep 25;32(9):1005-1011. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2018-0484. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 31323005
-
Short-term effects of gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogue treatment on leptin, ghrelin and peptide YY in girls with central precocious puberty.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Mar 1;34(4):479-484. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2020-0470. Print 2021 Apr 27. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 33655737
-
Leptin changes in Taiwanese girls with central precocious puberty before and during the GnRH agonist treatment.Acta Paediatr Taiwan. 2005 Sep-Oct;46(5):278-83. Acta Paediatr Taiwan. 2005. PMID: 16640001
-
Gonadotropin releasing hormone agonist treatment for central precocious puberty.Horm Res. 1999;51 Suppl 3:64-9. doi: 10.1159/000053164. Horm Res. 1999. PMID: 10592446 Review.
-
Alterations in Appetite-Regulating Hormones in Girls with Central Early or Precocious Puberty.Nutrients. 2023 Oct 9;15(19):4306. doi: 10.3390/nu15194306. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37836591 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Resistance and Endurance Training on Ghrelin and Plasma Leptin Levels in Overweight and Obese Subjects.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 24;25(15):8067. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158067. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic Review: Does Exercise Training Influence Ghrelin Levels?Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 15;26(10):4753. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104753. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429895 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin, Ghrelin, Irisin, Asprosin and Subfatin Changes in Obese Women: Effect of Exercise and Different Nutrition Types.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Jul 10;60(7):1118. doi: 10.3390/medicina60071118. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39064547 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources