A DNA nanodevice for mapping sodium at single-organelle resolution
- PMID: 37735265
- PMCID: PMC11004682
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-023-01950-1
A DNA nanodevice for mapping sodium at single-organelle resolution
Abstract
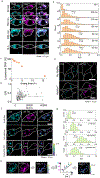
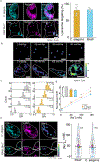
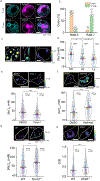
Cellular sodium ion (Na+) homeostasis is integral to organism physiology. Our current understanding of Na+ homeostasis is largely limited to Na+ transport at the plasma membrane. Organelles may also contribute to Na+ homeostasis; however, the direction of Na+ flow across organelle membranes is unknown because organellar Na+ cannot be imaged. Here we report a pH-independent, organelle-targetable, ratiometric probe that reports lumenal Na+. It is a DNA nanodevice containing a Na+-sensitive fluorophore, a reference dye and an organelle-targeting domain. By measuring Na+ at single endosome resolution in mammalian cells and Caenorhabditis elegans, we discovered that lumenal Na+ levels in each stage of the endolysosomal pathway exceed cytosolic levels and decrease as endosomes mature. Further, we find that lysosomal Na+ levels in nematodes are modulated by the Na+/H+ exchanger NHX-5 in response to salt stress. The ability to image subcellular Na+ will unveil mechanisms of Na+ homeostasis at an increased level of cellular detail.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests. YK is a co-founder of Esya Inc and MacroLogic Inc that use DNA nanodevices to develop diagnostics and therapeutics respectively.
Figures

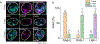





References
-
- Nass R, Cunningham KW & Rao R Intracellular sequestration of sodium by a novel Na+/H+ exchanger in yeast is enhanced by mutations in the plasma membrane H+-ATPase. Insights into mechanisms of sodium tolerance. J. Biol. Chem 272, 26145–26152 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Nass R & Rao R Novel localization of a Na+/H+ exchanger in a late endosomal compartment of yeast. Implications for vacuole biogenesis. J. Biol. Chem 273, 21054–21060 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Orlowski J & Grinstein S Na+/H+ exchangers. Compr. Physiol 1, 2083–2100 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Pedersen SF & Counillon L The SLC9A-C Mammalian Na+/H+ Exchanger Family: Molecules, Mechanisms, and Physiology. Physiol. Rev 99, 2015–2113 (2019). - PubMed
Methods only references
-
- Ellison DH & Welling P Insights into Salt Handling and Blood Pressure. N. Engl. J. Med 385, 1981–1993 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Müller DN, Wilck N, Haase S, Kleinewietfeld M & Linker RA Sodium in the microenvironment regulates immune responses and tissue homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol 19, 243–254 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM147197/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS112139/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS114428/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL161825/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 GM149751/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DP1GM149751/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- 1R01GM147197-01/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- DP1GM149751/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- DP1GM149751/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- DP1GM149751/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- DP1GM149751/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- DP1GM149751/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- DP1GM149751/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- 1R01GM147197-01/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- 1R01NS112139-01A1/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- 1R21NS114428-01/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- R21HL161825-01A1/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- RGP0032/2022/Human Frontier Science Program (HFSP)
- FA9550-19-0003/United States Department of Defense | United States Air Force | AFMC | Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AF Office of Scientific Research)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

