Structural basis of the activation of TRPV5 channels by long-chain acyl-Coenzyme-A
- PMID: 37735536
- PMCID: PMC10514044
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-41577-z
Structural basis of the activation of TRPV5 channels by long-chain acyl-Coenzyme-A
Abstract
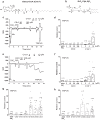
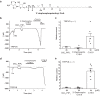
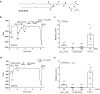
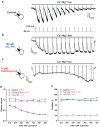
Long-chain acyl-coenzyme A (LC-CoA) is a crucial metabolic intermediate that plays important cellular regulatory roles, including activation and inhibition of ion channels. The structural basis of ion channel regulation by LC-CoA is not known. Transient receptor potential vanilloid 5 and 6 (TRPV5 and TRPV6) are epithelial calcium-selective ion channels. Here, we demonstrate that LC-CoA activates TRPV5 and TRPV6 in inside-out patches, and both exogenously supplied and endogenously produced LC-CoA can substitute for the natural ligand phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P2) in maintaining channel activity in intact cells. Utilizing cryo-electron microscopy, we determined the structure of LC-CoA-bound TRPV5, revealing an open configuration with LC-CoA occupying the same binding site as PI(4,5)P2 in previous studies. This is consistent with our finding that PI(4,5)P2 could not further activate the channels in the presence of LC-CoA. Our data provide molecular insights into ion channel regulation by a metabolic signaling molecule.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structural basis of TRPV5 regulation by physiological and pathophysiological modulators.Cell Rep. 2022 Apr 26;39(4):110737. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110737. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 35476976 Free PMC article.
-
What structures did, and did not, reveal about the function of the epithelial Ca2+ channels TRPV5 and TRPV6.Cell Calcium. 2022 Sep;106:102620. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2022.102620. Epub 2022 Jul 3. Cell Calcium. 2022. PMID: 35834842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphoinositide Regulation of TRP Channels: A Functional Overview in the Structural Era.Annu Rev Physiol. 2024 Feb 12;86:329-355. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-042022-013956. Epub 2023 Oct 23. Annu Rev Physiol. 2024. PMID: 37871124 Review.
-
Structural insights on TRPV5 gating by endogenous modulators.Nat Commun. 2018 Oct 10;9(1):4198. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06753-6. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30305626 Free PMC article.
-
Long chain CoA esters as competitive antagonists of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate activation in Kir channels.J Biol Chem. 2005 Sep 2;280(35):30760-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M503503200. Epub 2005 Jun 24. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15980413
Cited by
-
Molecular pharmacology of the onco-TRP channel TRPV6.Channels (Austin). 2023 Dec;17(1):2266669. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2023.2266669. Epub 2023 Oct 15. Channels (Austin). 2023. PMID: 37838981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphatidic acid is an endogenous negative regulator of PIEZO2 channels and mechanical sensitivity.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 2:2024.03.01.582964. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.01.582964. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 15;15(1):7020. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51181-4. PMID: 38464030 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Structural mechanism of TRPV5 inhibition by econazole.Structure. 2024 Feb 1;32(2):148-156.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2023.11.012. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Structure. 2024. PMID: 38141613 Free PMC article.
-
Bidirectional Allosteric Coupling between PIP2 Binding and the Pore of the Oncochannel TRPV6.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 3;25(1):618. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010618. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38203789 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular details of ruthenium red pore block in TRPV channels.EMBO Rep. 2024 Feb;25(2):506-523. doi: 10.1038/s44319-023-00050-0. Epub 2024 Jan 15. EMBO Rep. 2024. PMID: 38225355 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shrago E. Long-chain acyl-CoA as a multi-effector ligand in cellular metabolism. J. Nutr. 2000;130:290S–293S. - PubMed
-
- Larsson O, Deeney JT, Branstrom R, Berggren PO, Corkey BE. Activation of the ATP-sensitive K+ channel by long chain acyl-CoA. A role in modulation of pancreatic beta-cell glucose sensitivity. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:10623–10626. - PubMed
-
- Liu GX, Hanley PJ, Ray J, Daut J. Long-chain acyl-coenzyme A esters and fatty acids directly link metabolism to KATP channels in the heart. Circ. Res. 2001;88:918–924. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

