Defining E3 ligase-substrate relationships through multiplex CRISPR screening
- PMID: 37735597
- PMCID: PMC10567573
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-023-01229-2
Defining E3 ligase-substrate relationships through multiplex CRISPR screening
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Defining E3 ligase-substrate relationships through multiplex CRISPR screening.Nat Cell Biol. 2024 Feb;26(2):305. doi: 10.1038/s41556-023-01336-0. Nat Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38114738 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
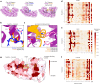
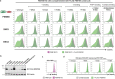
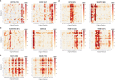
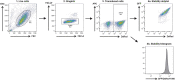
Specificity within the ubiquitin-proteasome system is primarily achieved through E3 ubiquitin ligases, but for many E3s their substrates-and in particular the molecular features (degrons) that they recognize-remain largely unknown. Current approaches for assigning E3s to their cognate substrates are tedious and low throughput. Here we developed a multiplex CRISPR screening platform to assign E3 ligases to their cognate substrates at scale. A proof-of-principle multiplex screen successfully performed ~100 CRISPR screens in a single experiment, refining known C-degron pathways and identifying an additional pathway through which Cul2FEM1B targets C-terminal proline. Further, by identifying substrates for Cul1FBXO38, Cul2APPBP2, Cul3GAN, Cul3KLHL8, Cul3KLHL9/13 and Cul3KLHL15, we demonstrate that the approach is compatible with pools of full-length protein substrates of varying stabilities and, when combined with site-saturation mutagenesis, can assign E3 ligases to their cognate degron motifs. Thus, multiplex CRISPR screening will accelerate our understanding of how specificity is achieved within the ubiquitin-proteasome system.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S.J.E. is a founder of MAZE Therapeutics, Mirimus, TSCAN Therapeutics and ImmuneID, and serves on the scientific advisory board of Homology Medicines, TSCAN Therapeutics and MAZE Therapeutics; none of these associations impacts this work. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures














References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

