Optimal delivery of RNA interference by viral vectors for cancer therapy
- PMID: 37735876
- PMCID: PMC10638062
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.09.012
Optimal delivery of RNA interference by viral vectors for cancer therapy
Abstract
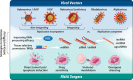
In recent years, there has been a surge in the innovative modification and application of the viral vector-based gene therapy field. Significant and consistent improvements in the engineering, delivery, and safety of viral vectors have set the stage for their application as RNA interference (RNAi) delivery tools. Viral vector-based delivery of RNAi has made remarkable breakthroughs in the treatment of several debilitating diseases and disorders (e.g., neurological diseases); however, their novelty has yet to be fully applied and utilized for the treatment of cancer. This review highlights the most promising and emerging viral vector delivery tools for RNAi therapeutics while discussing the variables limiting their success and suitability for cancer therapy. Specifically, we outline different integrating and non-integrating viral platforms used for gene delivery, currently employed RNAi targets for anti-cancer effect, and various strategies used to optimize the safety and efficacy of these RNAi therapeutics. Most importantly, we provide great insight into what challenges exist in their application as cancer therapeutics and how these challenges can be effectively navigated to advance the field.
Keywords: AAV; AV; DNA viruses; HSV; RNA interference; RNA viruses; RNAi therapeutics; VSV; adeno-associated virus; adenovirus; cancer therapeutics; herpes simplex virus; integrating viruses; microRNA; non-replicating viruses; oncolytic viruses; replicating viruses; retroviruses; short hairpin RNA; silencing RNA; vesicular stomatitis virus; viral vectors.
Copyright © 2023 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The design of vectors for RNAi delivery system.Curr Pharm Des. 2008;14(13):1327-40. doi: 10.2174/138161208799316357. Curr Pharm Des. 2008. PMID: 18537656 Review.
-
Expression of RNA interference triggers from an oncolytic herpes simplex virus results in specific silencing in tumour cells in vitro and tumours in vivo.BMC Cancer. 2010 Sep 13;10:486. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-486. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20836854 Free PMC article.
-
Non-viral delivery of RNA interference targeting cancer cells in cancer gene therapy.Curr Gene Ther. 2012 Aug;12(4):275-84. doi: 10.2174/156652312802083576. Curr Gene Ther. 2012. PMID: 22856602 Review.
-
Are Viral Vectors Any Good for RNAi Antiviral Therapy?Viruses. 2020 Oct 20;12(10):1189. doi: 10.3390/v12101189. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 33092124 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular therapeutics of cancer by means of electroporation-based transfer of siRNAs and EBV-based expression vectors.Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2009 Jun 1;1(1):316-31. doi: 10.2741/E31. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2009. PMID: 19482649 Review.
Cited by
-
Research progress of novel anti-tumor drug formulations.Front Oncol. 2024 Dec 16;14:1507958. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1507958. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39737395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural biomimetic nano-system for drug delivery in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a literature review of the last 5 years.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 May 9;11:1385123. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1385123. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38784236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High throughput screen identifies lysosomal acid phosphatase 2 (ACP2) to regulate IFN-1 responses to potentiate oncolytic VSV∆51 activity.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 16;14(1):28284. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76855-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39550388 Free PMC article.
-
Role and Therapeutic Potential of miR-301b-3p in Regulating the PI3K-AKT Pathway via PIK3CB in Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Jul 30;18:10235-10251. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S521536. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40756418 Free PMC article.
-
Hsa_piR_016975 Is a Novel Target of Nanotherapy that Boosts Hepatoma Progression and Sorafenib Resistance by Abating Maspin/GPX4-Mediated Ferroptosis.Biomater Res. 2025 Jul 2;29:0225. doi: 10.34133/bmr.0225. eCollection 2025. Biomater Res. 2025. PMID: 40606680 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Montgomery M.K. In: RNA Interference, Editing, and Modification. Gott J.M., editor. Humana Press; 2004. RNA Interference; pp. 3–21. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

