Silver-integrated EDM processing of TiAl6V4 implant material has antibacterial capacity while optimizing osseointegration
- PMID: 37736105
- PMCID: PMC10509668
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.08.019
Silver-integrated EDM processing of TiAl6V4 implant material has antibacterial capacity while optimizing osseointegration
Abstract
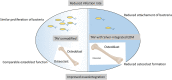
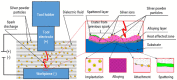
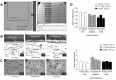
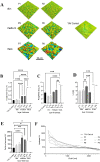
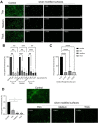
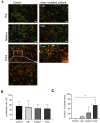
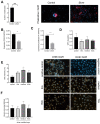
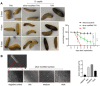
Periprosthetic joint infections (PJI) are a common reason for orthopedic revision surgeries. It has been shown that the silver surface modification of a titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) by PMEDM (powder mixed electrical discharge machining) exhibits an antibacterial effect on Staphylococcus spp. adhesion. Whether the thickness of the silver-modified surface influences the adhesion and proliferation of bacteria as well as the ossification processes and in-vivo antibacterial capacity has not been investigated before. Therefore, the aim of this work is to investigate the antibacterial effect as well as the in vitro ossification process depending on the thickness of PMEDM silver modified surfaces. The attachment of S. aureus on the PMEDM modified surfaces was significantly lower than on comparative control samples, independently of the tested surface properties. Bacterial proliferation, however, was not affected by the silver content in the surface layer. We observed a long-term effect of antibacterial capacity in vitro, as well as in vivo. An induction of ROS, as indicator for oxidative stress, was observed in the bacteria, but not in osteoblast-like cells. No influence on the in vitro osteoblast function was observed, whereas osteoclast formation was drastically reduced on the silver surface. No changes in cell death, the metabolic activity and oxidative stress was measured in osteoblasts. We show that already small amounts of silver exhibit a significant antibacterial capacity while not influencing the osteoblast function. Therefore, PMEDM using silver nano-powder admixed to the dielectric represents a promising technology to shape and concurrently modify implant surfaces to reduce infections while at the same time optimizing bone ingrowth of endoprosthesis.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial or personal interest or belief that could affect their objectivity with regard to the present manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microbiological and Cellular Evaluation of a Fluorine-Phosphorus-Doped Titanium Alloy, a Novel Antibacterial and Osteostimulatory Biomaterial with Potential Applications in Orthopedic Surgery.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 Jan 9;85(2):e02271-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02271-18. Print 2019 Jan 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30367003 Free PMC article.
-
Improved osseointegration of 3D printed Ti-6Al-4V implant with a hierarchical micro/nano surface topography: An in vitro and in vivo study.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021 Jan;118:111505. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.111505. Epub 2020 Sep 11. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021. PMID: 33255064
-
Biofunctionalization of selective laser melted porous titanium using silver and zinc nanoparticles to prevent infections by antibiotic-resistant bacteria.Acta Biomater. 2020 Apr 15;107:325-337. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.02.044. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32145392
-
Osteoblast response and osseointegration of a Ti-6Al-4V alloy implant incorporating strontium.Acta Biomater. 2010 Jul;6(7):2843-51. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2010.01.017. Epub 2010 Jan 18. Acta Biomater. 2010. PMID: 20085830
-
A systematic review on powder mixed electrical discharge machining.Heliyon. 2019 Dec 2;5(12):e02963. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02963. eCollection 2019 Dec. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31872127 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Powder Bed Fusion 3D Printing in Precision Manufacturing for Biomedical Applications: A Comprehensive Review.Materials (Basel). 2024 Feb 5;17(3):769. doi: 10.3390/ma17030769. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38591985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silver/Graphene Oxide Nanostructured Coatings for Modulating the Microbial Susceptibility of Fixation Devices Used in Knee Surgery.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 23;25(1):246. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010246. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zimmerli ATaW. Diagnosis and treatment of implant-associated septic arthritis and osteomyelitis. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2008;10:394–403. - PubMed
-
- Fehring T.K.O.S., Caltin T.F., Mason J.B. Articulating versus static spacers in revision total knee arthroplasty for sepsis. Orthopaed. Relat. Res. 2000;380:9–16. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg Alfred L., K I.C., Furuno Koji, Fagan Julie M., Baracos Vickie. Activation of protein breakdown and prostaglandin E2 production in rat skeletal muscle in fever is signaled by a macrophage product distinct from interleukin 1 or other known monokines. J. Clin. Invest. 1988;81:1378–1383. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Smucny M., Menendez M.E., Ring D., Feeley B.T., Zhang A.L. Inpatient surgical site infection after shoulder arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015;24(5):747–753. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

