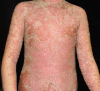
The update of treatment strategies in pediatrics with generalized pustular psoriasis in China
- PMID: 37736368
- PMCID: PMC10509407
- DOI: 10.1002/ped4.12395
The update of treatment strategies in pediatrics with generalized pustular psoriasis in China
Abstract
Generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) is a severe subtype of psoriasis, commonly combined with systemic inflammation. Gene mutations have been found to be associated with GPP and vary by ethnicity. Systemic treatments are usually required for the severity and potential complications of GPP. However, there is no common consensus in China, especially among pediatric patients, whose data are scarce. Acitretin, methotrexate, and cyclosporine are widely used in pediatrics with GPP, while the adverse effects should be highlighted. The emergence of different biological agents brings us into a new era. This article discusses the genetic background of Chinese patients and demonstrates the evidence of treatment in pediatrics with GPP.
Keywords: Generalized pustular psoriasis; Pediatrics; Treatment.
© 2023 Chinese Medical Association. Pediatric Investigation published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Futang Research Center of Pediatric Development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical characteristics of Japanese pustular psoriasis: A multicenter observational study.J Dermatol. 2022 Jan;49(1):142-150. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.16217. Epub 2021 Nov 1. J Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 34723399
-
Juvenile generalized pustular psoriasis is a chronic recalcitrant disease: an analysis of 27 patients seen in a tertiary hospital in Johor, Malaysia.Int J Dermatol. 2017 Apr;56(4):392-399. doi: 10.1111/ijd.13489. Epub 2017 Feb 14. Int J Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 28194751
-
Pustular Psoriasis: A Narrative Review of Recent Developments in Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Options.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021 Dec;11(6):1917-1929. doi: 10.1007/s13555-021-00612-x. Epub 2021 Oct 9. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021. PMID: 34626330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Successful treatment of paediatric generalized pustular psoriasis with secukinumab: a case series.J Dermatolog Treat. 2022 May;33(3):1769-1773. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2021.1899111. Epub 2021 Mar 11. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022. PMID: 33706651
-
Current management of generalized pustular psoriasis.Exp Dermatol. 2023 Aug;32(8):1204-1218. doi: 10.1111/exd.14765. Epub 2023 Mar 1. Exp Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 36779681 Review.
Cited by
-
Generalized pustular psoriasis in a toddler with IL36RN mutation: a case report.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 20;15:1337799. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1337799. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38571950 Free PMC article.
-
Successful Treatment of Pediatric Generalized Pustular Psoriasis (GPP) with Spesolimab: 5 Case Reports and Evaluations of Circulating IL-36 Levels.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Nov 4;17:8199-8206. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S485077. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39525315 Free PMC article.
-
Etanercept: A viable treatment option for young children with generalized pustular psoriasis.Pediatr Investig. 2024 Aug 12;8(4):295-298. doi: 10.1002/ped4.12448. eCollection 2024 Dec. Pediatr Investig. 2024. PMID: 39720279 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources