Profiling the polyadenylated transcriptome of extracellular vesicles with long-read nanopore sequencing
- PMID: 37736705
- PMCID: PMC10514964
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-023-09552-6
Profiling the polyadenylated transcriptome of extracellular vesicles with long-read nanopore sequencing
Abstract
Background: While numerous studies have described the transcriptomes of extracellular vesicles (EVs) in different cellular contexts, these efforts have typically relied on sequencing methods requiring RNA fragmentation, which limits interpretations on the integrity and isoform diversity of EV-targeted RNA populations. It has been assumed that mRNA signatures in EVs are likely to be fragmentation products of the cellular mRNA material, and the extent to which full-length mRNAs are present within EVs remains to be clarified.
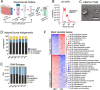
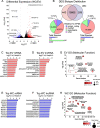
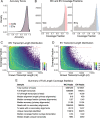
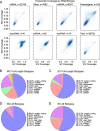
Results: Using long-read nanopore RNA sequencing, we sought to characterize the full-length polyadenylated (poly-A) transcriptome of EVs released by human chronic myelogenous leukemia K562 cells. We detected 443 and 280 RNAs that were respectively enriched or depleted in EVs. EV-enriched poly-A transcripts consist of a variety of biotypes, including mRNAs, long non-coding RNAs, and pseudogenes. Our analysis revealed that 10.58% of all EV reads, and 18.67% of all cellular (WC) reads, corresponded to known full-length transcripts, with mRNAs representing the largest biotype for each group (EV = 58.13%, WC = 43.93%). We also observed that for many well-represented coding and non-coding genes, diverse full-length transcript isoforms were present in EV specimens, and these isoforms were reflective-of but often in different ratio compared to cellular samples.
Conclusion: This work provides novel insights into the compositional diversity of poly-A transcript isoforms enriched within EVs, while also underscoring the potential usefulness of nanopore sequencing to interrogate secreted RNA transcriptomes.
Keywords: Extracellular vesicles; Long-Read RNA Sequencing; Nanopore sequencing; Poly-A; Polyadenylated transcriptome; RNA-seq; Transcript Isoforms; Transcriptomics; lncRNA; mRNA.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Théry C, Witwer KW, Aikawa E, Alcaraz MJ, Anderson JD, Andriantsitohaina R, Antoniou A, Arab T, Archer F, Atkin-Smith GK, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7(1):1535750. - PMC - PubMed
-
- van Niel G, D'Angelo G, Raposo G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(4):213–228. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

