Engineering exosomes derived from subcutaneous fat MSCs specially promote cartilage repair as miR-199a-3p delivery vehicles in Osteoarthritis
- PMID: 37736726
- PMCID: PMC10515007
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-023-02086-9
Engineering exosomes derived from subcutaneous fat MSCs specially promote cartilage repair as miR-199a-3p delivery vehicles in Osteoarthritis
Abstract
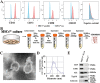
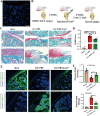
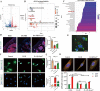
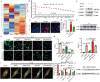
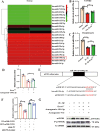
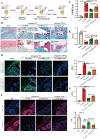
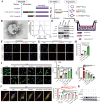
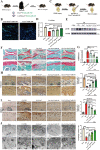
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease involving cartilage. Exosomes derived from Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) therapy improves articular cartilage repair, but subcutaneous fat (SC) stromal cells derived exosomes (MSCsSC-Exos), especially engineering MSCsSC-Exos for drug delivery have been rarely reported in OA therapy. This objective of this study was to clarify the underlying mechanism of MSCsSC-Exos on cartilage repair and therapy of engineering MSCsSC-Exos for drug delivery in OA. MSCsSC-Exos could ameliorate the pathological severity degree of cartilage via miR-199a-3p, a novel molecular highly enriched in MSCsSC-Exos, which could mediate the mTOR-autophagy pathway in OA rat model. Intra-articular injection of antagomiR-199a-3p dramatically attenuated the protective effect of MSCsSC-Exos-mediated on articular cartilage in vivo. Furthermore, to achieve the superior therapeutic effects of MSCsSC-Exos on injured cartilage, engineering exosomes derived from MSCsSC as the chondrocyte-targeting miR-199a-3p delivery vehicles were investigated in vitro and in vivo. The chondrocyte-binding peptide (CAP) binding MSCsSC-Exos could particularly deliver miR-199a-3p into the chondrocytes in vitro and into deep articular tissues in vivo, then exert the excellent protective effect on injured cartilage in DMM-induced OA mice. As it is feasible to obtain human subcutaneous fat from healthy donors by liposuction operation in clinic, meanwhile engineering MSCsSC-Exos to realize targeted delivery of miR-199a-3p into chondrocytes exerted excellent therapeutic effects in OA animal model in vivo. Through combining MSCsSC-Exos therapy and miRNA therapy via an engineering approach, we develop an efficient MSCsSC-Exos-based strategy for OA therapy and promote the application of targeted-MSCsSC-Exos for drug delivery in the future.
Keywords: Autophagy; Cartilage-targeted; Engineering exosomes; Osteoarthritis; miR-199a-3p.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

