Lymph node ratio and hematological parameters predict relapse-free survival in patients with high grade rectal neuroendocrine neoplasms after radical resection: a multicenter prognostic study
- PMID: 37736728
- PMCID: PMC10515051
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-023-03144-0
Lymph node ratio and hematological parameters predict relapse-free survival in patients with high grade rectal neuroendocrine neoplasms after radical resection: a multicenter prognostic study
Abstract
Background: The prognostic nutritional index (PNI), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and lymph node ratio (LNR) are reportedly related to prognosis. The aim of this study was to elucidate the clinical importance of the LNR and hematological parameters in patients with high grade rectal neuroendocrine neoplasms (HG-RNENs) who were undergoing radical resection.
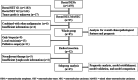
Methods: We reviewed the medical records of patients with HG-RNENs from 17 large-scale medical centers in China (January 1, 2010-April 30, 2022). A nomogram was constructed by using a proportional hazard model. Bootstrap method was used to draw calibration plots to validate the reproducibility of the model. Concordance index (C-Index), decision curve analysis (DCA), and time-dependent area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (TD-AUC) analysis were used to compare the prognostic predictive power of the new model with American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM staging and European Neuroendocrine Tumor Society (ENETS) TNM staging.
Results: A total of 85 patients with HG-RNENs were enrolled in this study. In the 45 patients with HG-RNENs who underwent radical resection, PNI ≤ 49.13 (HR: 3.997, 95% CI: 1.379-11.581, P = 0.011), ALP > 100.0 U/L (HR: 3.051, 95% CI: 1.011-9.205, P = 0.048), and LNR > 0.40 (HR: 6.639, 95% CI: 2.224-19.817, P = 0.0007) were independent predictors of relapse-free survival. The calibration plots suggested that the nomogram constructed based on the three aforementioned factors had good reproducibility. The novel nomogram revealed a C-index superior to AJCC TNM staging (0.782 vs 0.712) and ENETS TNM staging (0.782 vs 0.657). Also, the new model performed better compared to AJCC TNM staging and ENETS TNM staging in DCA and TD-AUC analyses.
Conclusions: LNR, ALP, and PNI were independent prognostic factors in patients with HG-RNENs after radical resection, and the combined indicator had better predictive efficacy compared with AJCC TNM staging and ENETS TNM staging.
Keywords: Carcinoma; Neuroendocrine; Nomograms; Rectal neoplasms; Recurrence.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Rindi G, Arnold R, Bosman F, et al. WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. 4. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC); 2010.
-
- Fang C, Wang W, Zhang Y, Feng X, Sun J, Zeng Y, Chen Y, Li Y, Chen M, Zhou Z, Chen J. Clinicopathologic characteristics and prognosis of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms: a multicenter study in South China. Chin J Cancer. 2017;36(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s40880-017-0218-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

