Long Non-Coding RNA TUG1 Gene Polymorphism and TUG1 Expression Level as Molecular Biomarkers of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis
- PMID: 37736902
- PMCID: PMC10514853
- DOI: 10.3390/ncrna9050056
Long Non-Coding RNA TUG1 Gene Polymorphism and TUG1 Expression Level as Molecular Biomarkers of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis
Abstract
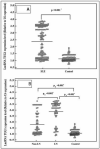
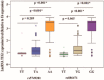
Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) TUG1 acts as a proto-oncogene, allowing the proliferation of tumor cells, and it has been related to inflammation. Therefore, we aimed in this study to investigate for the first time the role of TUG1 gene polymorphism and the TUG1 level as biomarkers in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and their link to lupus nephritis 145 SLE. A total of 145 healthy controls were subjected to clinical and laboratory evaluation. The disease activity was assessed by the SLE disease activity index (SLEDAI) score. SLE patients were divided into two subgroups according to the presence of lupus nephritis. The TUG1 gene polymorphisms rs5749201 and rs886471 were determined by Sanger sequencing, and TUG1 expression was assessed by qRT-PCR. There was a significant increase in the risk of SLE AA, TA, dominant genotypes, and the A allele of rs5749201 (p < 0.001) by 4.9-, 10.1-, 6.5-, and 2.5-fold in comparison to the relative control. GG and TG, dominant genotypes and the G allele of rs886471 (p < 0.01) increased the risk by 5.09-, 11.9-, 6.5-, and 2.6-fold. AA, A allele, dominant and recessive rs5749201genotypes increased the risk of lupus nephritis by 16.6-, 7.4-, 7.1-, and 12.2-fold, respectively (p < 0.05). GG, dominant and recessive genotypes, and the G allele of rs886471 increased the risk of lupus nephritis by 17.04-, 7.8-, 9.4-, and 6.08-fold, respectively (p < 0.05). Additionally, the AG haplotype increased the risk of SLE and lupus nephritis by 2.7- and 7.8-fold, respectively. The AA rs5749201 and GG rs886471 variants are significantly associated with more severe disease (p < 0.001). TUG1 expression was significantly higher in SLE than in the control and in the lupus nephritis than in non-lupus nephritis cases (p < 0.05). Interestingly, AA rs5749201 and GG rs886471 were significantly associated with higher TUG1 levels (p < 0.001). It was also found that AA rs5749201 and high SLEDAI were predictors of lupus nephritis. Overall, our findings illustrated for the first time that TUG1 gene rs5749201 and rs886471 variants were associated with increased risk of SLE, more severe disease, and lupus nephritis, and the TUG1 level could be used as a diagnostic biomarker of SLE and lupus nephritis.
Keywords: TUG1 expression; lncRNA TUG1 SNPs; lupus nephritis; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of the Expression Levels of Long-Chain Noncoding RNA TUG1 and Its Gene Polymorphisms with Knee Osteoarthritis.Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2021 Feb;25(2):102-110. doi: 10.1089/gtmb.2020.0208. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2021. PMID: 33596137
-
Clinical significance of reduced expression of lncRNA TUG1 in the peripheral blood of systemic lupus erythematosus patients.Int J Rheum Dis. 2020 Mar;23(3):428-434. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13786. Epub 2020 Jan 15. Int J Rheum Dis. 2020. PMID: 31944629
-
CD14 (C-159T) polymorphism is associated with increased susceptibility to SLE, and plasma levels of soluble CD14 is a novel biomarker of disease activity: A hospital-based case-control study.Lupus. 2021 Feb;30(2):219-227. doi: 10.1177/0961203320972799. Epub 2020 Nov 11. Lupus. 2021. PMID: 33176568
-
Value of HLA-DR genotype in systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis: a meta-analysis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2015 Jan;18(1):17-28. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.12528. Epub 2014 Dec 26. Int J Rheum Dis. 2015. PMID: 25546242 Review.
-
Association of FcγRIIA-R/H131 polymorphism and systemic lupus erythematosus lupus nephritis risk: A meta-analysis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2020 Jul;23(7):853-867. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13815. Epub 2020 Mar 18. Int J Rheum Dis. 2020. PMID: 32189478 Review.
References
-
- Izmirly P.M., Wan I., Sahl S., Buyon J.P., Belmont H.M., Salmon J.E., Askanase A., Bathon J.M., Geraldino-Pardilla L., Ali Y., et al. The Incidence and Prevalence of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in New York County (Manhattan), New York: The Manhattan Lupus Surveillance Program. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017;69:2006–2017. doi: 10.1002/art.40192. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

