Deep Learning-Based Versus Iterative Image Reconstruction for Unenhanced Brain CT: A Quantitative Comparison of Image Quality
- PMID: 37736983
- PMCID: PMC10514884
- DOI: 10.3390/tomography9050130
Deep Learning-Based Versus Iterative Image Reconstruction for Unenhanced Brain CT: A Quantitative Comparison of Image Quality
Abstract
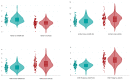
This exploratory retrospective study aims to quantitatively compare the image quality of unenhanced brain computed tomography (CT) reconstructed with an iterative (AIDR-3D) and a deep learning-based (AiCE) reconstruction algorithm. After a preliminary phantom study, AIDR-3D and AiCE reconstructions (0.5 mm thickness) of 100 consecutive brain CTs acquired in the emergency setting on the same 320-detector row CT scanner were retrospectively analyzed, calculating image noise reduction attributable to the AiCE algorithm, artifact indexes in the posterior cranial fossa, and contrast-to-noise ratios (CNRs) at the cortical and thalamic levels. In the phantom study, the spatial resolution of the two datasets proved to be comparable; conversely, AIDR-3D reconstructions showed a broader noise pattern. In the human study, median image noise was lower with AiCE compared to AIDR-3D (4.7 vs. 5.3, p < 0.001, median 19.6% noise reduction), whereas AIDR-3D yielded a lower artifact index than AiCE (7.5 vs. 8.4, p < 0.001). AiCE also showed higher median CNRs at the cortical (2.5 vs. 1.8, p < 0.001) and thalamic levels (2.8 vs. 1.7, p < 0.001). These results highlight how image quality improvements granted by deep learning-based (AiCE) and iterative (AIDR-3D) image reconstruction algorithms vary according to different brain areas.
Keywords: brain computed tomography; deep learning-based reconstruction algorithms; image noise; image quality; iterative reconstruction algorithms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Agostini A., Borgheresi A., Carotti M., Ottaviani L., Badaloni M., Floridi C., Giovagnoni A. Third-generation iterative reconstruction on a dual-source, high-pitch, low-dose chest CT protocol with tin filter for spectral shaping at 100 kV: A study on a small series of COVID-19 patients. Radiol. Med. 2021;126:388–398. doi: 10.1007/s11547-020-01298-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

