E2F1 Mediates SOX17 Deficiency-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension
- PMID: 37737027
- PMCID: PMC10591929
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.123.21241
E2F1 Mediates SOX17 Deficiency-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension
Abstract
Background: Rare genetic variants and genetic variation at loci in an enhancer in SOX17 (SRY-box transcription factor 17) are identified in patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) and PAH with congenital heart disease. However, the exact role of genetic variants or mutations in SOX17 in PAH pathogenesis has not been reported.
Methods: SOX17 expression was evaluated in the lungs and pulmonary endothelial cells (ECs) of patients with idiopathic PAH. Mice with Tie2Cre-mediated Sox17 knockdown and EC-specific Sox17 deletion were generated to determine the role of SOX17 deficiency in the pathogenesis of PAH. Human pulmonary ECs were cultured to understand the role of SOX17 deficiency. Single-cell RNA sequencing, RNA-sequencing analysis, and luciferase assay were performed to understand the underlying molecular mechanisms of SOX17 deficiency-induced PAH. E2F1 (E2F transcription factor 1) inhibitor HLM006474 was used in EC-specific Sox17 mice.
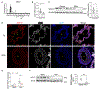
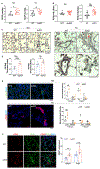
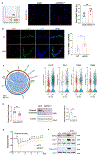
Results: SOX17 expression was downregulated in the lung and pulmonary ECs from patients with idiopathic PAH. Mice with Tie2Cre-mediated Sox17 knockdown and EC-specific Sox17 deletion induced spontaneously mild pulmonary hypertension. Loss of endothelial Sox17 in EC exacerbated hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension in mice. Loss of SOX17 in lung ECs induced endothelial dysfunctions including upregulation of cell cycle programming, proliferative and antiapoptotic phenotypes, augmentation of paracrine effect on pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells, impaired cellular junction, and BMP (bone morphogenetic protein) signaling. E2F1 signaling was shown to mediate the SOX17 deficiency-induced EC dysfunction. Pharmacological inhibition of E2F1 in Sox17 EC-deficient mice attenuated pulmonary hypertension development.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrated that endothelial SOX17 deficiency induces pulmonary hypertension through E2F1. Thus, targeting E2F1 signaling represents a promising approach in patients with PAH.
Keywords: angiogenesis; endothelial cells; hypertension; mice; pulmonary artery.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Update of
-
E2F1 Mediates SOX17 Deficiency-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 16:2023.02.15.528740. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.15.528740. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Hypertension. 2023 Nov;80(11):2357-2371. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.123.21241. PMID: 36824855 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Humbert M, Kovacs G, Hoeper MM, Badagliacca R, Berger RMF, Brida M, Carlsen J, Coats AJS, Escribano-Subias P, Ferrari P, Ferreira DS, Ghofrani HA, Giannakoulas G, Kiely DG, Mayer E, Meszaros G, Nagavci B, Olsson KM, Pepke-Zaba J, Quint JK, Rådegran G, Simonneau G, Sitbon O, Tonia T, Toshner M, Vachiery JL, Vonk Noordegraaf A, Delcroix M, Rosenkranz S, ESC/ERS Scientific Document Group, Schwerzmann M, Dinh-Xuan AT, Bush A, Abdelhamid M, Aboyans V, Arbustini E, Asteggiano R, Barberà JA, Beghetti M, Čelutkienė J, Cikes M, Condliffe R, De Man F, Falk V, Fauchier L, Gaine S, Galié N, Gin-Sing W, Granton J, Grünig E, Hassoun PM, Hellemons M, Jaarsma T, Kjellström B, Klok FA, Konradi A, Koskinas KC, Kotecha D, Lang I, Lewis BS, Linhart A, Lip GYH, Løchen ML, Mathioudakis AG, Mindham R, Moledina S, Naeije R, Nielsen JC, Olschewski H, Opitz I, Petersen SE, Prescott E, Rakisheva A, Reis A, Ristić AD, Roche N, Rodrigues R, Selton-Suty C, Souza R, Swift AJ, Touyz RM, Ulrich S, Wilkins MR, Wort SJ. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. European Heart Journal. 2022;43:3618–3731. - PubMed
-
- Austin ED, Newman JH, Loyd JE, Phillips JA. Heritable and Idiopathic Forms of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. In: Emery and Rimoin’s Principles and Practice of Medical Genetics and Genomics. Elsevier; 2020. p. 439–462.
-
- Evans JDW, Girerd B, Montani D, Wang X-J, Galiè N, Austin ED, Elliott G, Asano K, Grünig E, Yan Y, Jing Z-C, Manes A, Palazzini M, Wheeler LA, Nakayama I, Satoh T, Eichstaedt C, Hinderhofer K, Wolf M, Rosenzweig EB, Chung WK, Soubrier F, Simonneau G, Sitbon O, Gräf S, Kaptoge S, Di Angelantonio E, Humbert M, Morrell NW. BMPR2 mutations and survival in pulmonary arterial hypertension: an individual participant data meta-analysis. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine. 2016;4:129–137. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Southgate L, Machado RD, Gräf S, Morrell NW. Molecular genetic framework underlying pulmonary arterial hypertension. Nature Reviews Cardiology. 2020;17:85–95. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

