Added value of CE-CT radiomics to predict high Ki-67 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 37737166
- PMCID: PMC10514983
- DOI: 10.1186/s12880-023-01069-4
Added value of CE-CT radiomics to predict high Ki-67 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to develop a computed tomography (CT) model to predict Ki-67 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and to examine the added value of radiomics to clinico-radiological features.
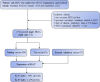
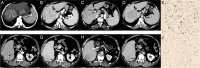
Methods: A total of 208 patients (training set, n = 120; internal test set, n = 51; external validation set, n = 37) with pathologically confirmed HCC who underwent contrast-enhanced CT (CE-CT) within 1 month before surgery were retrospectively included from January 2014 to September 2021. Radiomics features were extracted and selected from three phases of CE-CT images, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression (LASSO) was used to select features, and the rad-score was calculated. CE-CT imaging and clinical features were selected using univariate and multivariate analyses, respectively. Three prediction models, including clinic-radiologic (CR) model, rad-score (R) model, and clinic-radiologic-radiomic (CRR) model, were developed and validated using logistic regression analysis. The performance of different models for predicting Ki-67 expression was evaluated using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) and decision curve analysis (DCA).
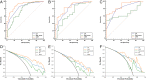
Results: HCCs with high Ki-67 expression were more likely to have high serum α-fetoprotein levels (P = 0.041, odds ratio [OR] 2.54, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.04-6.21), non-rim arterial phase hyperenhancement (P = 0.001, OR 15.13, 95% CI 2.87-79.76), portal vein tumor thrombus (P = 0.035, OR 3.19, 95% CI: 1.08-9.37), and two-trait predictor of venous invasion (P = 0.026, OR 14.04, 95% CI: 1.39-144.32). The CR model achieved relatively good and stable performance compared with the R model (AUC, 0.805 [95% CI: 0.683-0.926] vs. 0.678 [95% CI: 0.536-0.839], P = 0.211; and 0.805 [95% CI: 0.657-0.953] vs. 0.667 [95% CI: 0.495-0.839], P = 0.135) in the internal and external validation sets. After combining the CR model with the R model, the AUC of the CRR model increased to 0.903 (95% CI: 0.849-0.956) in the training set, which was significantly higher than that of the CR model (P = 0.0148). However, no significant differences were found between the CRR and CR models in the internal and external validation sets (P = 0.264 and P = 0.084, respectively).
Conclusions: Preoperative models based on clinical and CE-CT imaging features can be used to predict HCC with high Ki-67 expression accurately. However, radiomics cannot provide added value.
Keywords: Contrast-enhanced computed tomography; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Ki-67 expression; Radiomics.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Li H-H, Qi L-N, Ma L, Chen Z-S, Xiang B-D, Li L-Q. Effect of KI-67 positive cellular index on prognosis after hepatectomy in Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage A and B hepatocellular carcinoma with microvascular invasion. Onco Targets Ther. 2018;11:4747–4754. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S165244. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

