The long-term efficacy and safety of nilotinib in pediatric patients with CML: a 5-year update of the DIALOG study
- PMID: 37738125
- PMCID: PMC10711170
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023010122
The long-term efficacy and safety of nilotinib in pediatric patients with CML: a 5-year update of the DIALOG study
Abstract
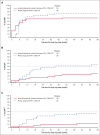
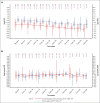
The efficacy and safety of nilotinib in pediatric patients with imatinib/dasatinib resistant/intolerant (R/I) or newly diagnosed (ND) Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP) was demonstrated in the phase 2, open-label DIALOG study. In this final analysis, long-term efficacy and safety are presented for patients who completed 66 cycles (of 28 days) of treatment with nilotinib (230 mg/m2 twice daily) or discontinued early. Overall, 59 patients were enrolled and 58 were treated (R/I, n = 33; ND, n = 25; median time on treatment: 60.5 and 51.9 months, respectively). In the R/I cohort, the cumulative major molecular response (MMR; BCR::ABL1 international scale [IS] ≤ 0.1%) rate was 60.6%, and no patients had a confirmed loss of MMR. Among ND patients, the best overall MMR rate was 76.0%; 3 patients had a confirmed loss of MMR. The cumulative molecular response MR4 (BCR::ABL1IS ≤ 0.01%) and MR4.5 (BCR::ABL1IS ≤ 0.0032%) rates by 66 cycles were 27.3% and 12.1% in the R/I cohort, and 56.0% and 44.0% in the ND cohort, respectively. The safety profile of nilotinib was consistent with those of earlier reports. No on-treatment deaths occurred. These long-term (up to ∼5 years) data support the efficacy and safety of nilotinib in pediatric patients with Ph+ CML-CP. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov.uk as #NCT01844765.
© 2023 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: N.H. has received research funding from Novartis and Pfizer; served on the data monitoring committee for Incyte and Novartis; participated on an advisory board for Stemline Therapeutics; and has been a consultant for Novartis. A.M. reports receiving lecture fees from Novartis. H.G. reports receiving lecture fees from Novartis. Z.K. reports receiving grants from Novartis. C.M.Z. reports serving as a consultant to Novartis and has obtained institutional funding from Bristol Myers Squibb and Pfizer for the development of other CML therapies. J.S. reports serving as a consultant to Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Tolmar Pharmaceuticals, and has received speaker fees from Tolmar Pharmaceuticals. M.I. and S.L. report employment at and ownership of stock in Novartis. K.T. reports employment at Novartis. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- European Medicines Agency Imatinib summary of opinion. 2013. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/smop-initial/chmp-summary-positiv...
-
- Gleevec (imatinib). Prescribing information. Novartis Pharmacueticals. 2022
-
- FDA Approves Dasatinib for Pediatric Patients With CML. FDA. 2017
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

