Intranasal mRNA-LNP vaccination protects hamsters from SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 37738334
- PMCID: PMC10516494
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adh1655
Intranasal mRNA-LNP vaccination protects hamsters from SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
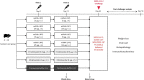
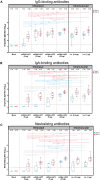
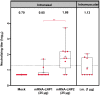
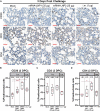
Intranasal vaccination represents a promising approach for preventing disease caused by respiratory pathogens by eliciting a mucosal immune response in the respiratory tract that may act as an early barrier to infection and transmission. This study investigated immunogenicity and protective efficacy of intranasally administered messenger RNA (mRNA)-lipid nanoparticle (LNP) encapsulated vaccines against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in Syrian golden hamsters. Intranasal mRNA-LNP vaccination systemically induced spike-specific binding [immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgA] and neutralizing antibodies. Intranasally vaccinated hamsters also had decreased viral loads in the respiratory tract, reduced lung pathology, and prevented weight loss after SARS-CoV-2 challenge. Together, this study demonstrates successful immunogenicity and protection against respiratory viral infection by an intranasally administered mRNA-LNP vaccine.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization, The top 10 causes of death (2020); www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death.
-
- World Health Organization, COVID-19 vaccine tracker and landscape (2022); www.who.int/publications/m/item/draft-landscape-of-covid-19-candidate-va....
-
- GBD 2016 Lower Respiratory Infections Collaborators , Estimates of the global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of lower respiratory infections in 195 countries, 1990-2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Infect. Dis. 18, 1191–1210 (2018). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) , Ten great public health achievements--worldwide, 2001–2010. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly Rep. 60, 814–818 (2011). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

