Atrial fibrillation cryoablation is an effective day case treatment: the UK PolarX vs. Arctic Front Advance experience
- PMID: 37738643
- PMCID: PMC10629714
- DOI: 10.1093/europace/euad286
Atrial fibrillation cryoablation is an effective day case treatment: the UK PolarX vs. Arctic Front Advance experience
Abstract
Aims: Pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) is the cornerstone of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation (AF). There are limited data on the PolarX Cryoballoon. The study aimed to establish the safety, efficacy, and feasibility of same day discharge for Cryoballoon PVI.
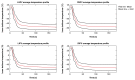
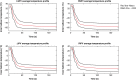
Methods and results: Multi-centre study across 12 centres. Procedural metrics, safety profile, and procedural efficacy of the PolarX Cryoballoon with the Arctic Front Advance (AFA) Cryoballoon were compared in a cohort large enough to provide definitive comparative data. A total of 1688 patients underwent PVI with cryoablation (50% PolarX and 50% AFA). Successful PVI was achieved with 1677 (99.3%) patients with 97.2% (n = 1641) performed as day case procedures with a complication rate of <1%. Safety, procedural metrics, and efficacy of the PolarX Cryoballoon were comparable with the AFA cohort. The PolarX Cryoballoon demonstrated a nadir temperature of -54.6 ± 7.6°C, temperature at 30 s of -38.6 ± 7.2°C, time to -40°C of 34.1 ± 13.7 s, and time to isolation of 49.8 ± 33.2 s. Independent predictors for achieving PVI included time to reach -40°C [odds ratio (OR) 1.34; P < 0.001] and nadir temperature (OR 1.24; P < 0.001) with an optimal cut-off of ≤34 s [area under the curve (AUC) 0.73; P < 0.001] and nadir temperature of ≤-54.0°C (AUC 0.71; P < 0.001), respectively.
Conclusions: This large-scale UK multi-centre study has shown that Cryoballoon PVI is a safe, effective day case procedure. PVI using the PolarX Cryoballoon was similarly safe and effective as the AFA Cryoballoon. The cryoablation metrics achieved with the PolarX Cryoballoon were different to that reported with the AFA Cryoballoon. Modified cryoablation targets are required when utilizing the PolarX Cryoballoon.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Cryoablation; Novel technology; Pulmonary vein isolation.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: R.J.H. has received speaker fees, consultancy fees, research, and educational grants from Medtronic and Biosense Webster. R.J.H., R.J.S., and S.H. are inventors of the STAR Mapping system and Founders of Rhythm AI. S.H. is a British Heart Foundation Clinical Intermediate Fellow and receives funding from the British Heart Foundation grant. C.A.M. has received research grants and consultancy fees from Boston Scientific and speaker and travel grants from Boston Scientific and Medtronic. M.D. has received research grant and speaker fees from Boston Scientific, consulting fees from Philips, and fellowship funding from Boston Scientific and Biosense Webster. J.P. has received consultancy fees from Medtronic and Boston Scientific. R.J.S. has received speaker and travel grants from Biosense Webster and research grants from Biosense Webster. R.J.H. has received travel grants for the purposes of attending conferences from Biosense Webster. The remaining authors have declared no conflicts of interest..
Figures

References
-
- Asad ZUA, Yousif A, Khan MS, Al-Khatib SM, Stavrakis S. Catheter ablation versus medical therapy for atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2019;12:e007414. - PubMed
-
- Andrade JG, Wells GA, Deyell MW, Bennett M, Essebag V, Champagne Jet al. Cryoablation or drug therapy for initial treatment of atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2021;384:305–15. - PubMed
-
- Verma A, Jiang CY, Betts TR, Chen J, Deisenhofer I, Mantovan Ret al. Approaches to catheter ablation for persistent atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2015;372:1812–22. - PubMed
-
- Kuck KH, Brugada J, Furnkranz A, Metzner A, Ouyang F, Chun KRet al. Cryoballoon or radiofrequency ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2016;374:2235–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

