Monte Carlo investigation of dose distribution of uniformly and non-uniformly loaded standard and notched eye plaques
- PMID: 37738654
- PMCID: PMC10691642
- DOI: 10.1002/acm2.14149
Monte Carlo investigation of dose distribution of uniformly and non-uniformly loaded standard and notched eye plaques
Abstract
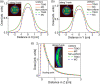
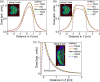
To investigate the effect of using non-uniform loading and notched plaques on dose distribution for eye plaques. Using EGSnrc Monte Carlo (MC) simulations, we investigate eye plaque dose distributions in water and in an anatomically representative eye phantom. Simulations were performed in accordance with TG43 formalism and compared against full MC simulations which account for inter-seed and inhomogeneity effects. For standard plaque configurations, uniformly and non-uniformly loaded plaque dose distributions in water showed virtually no difference between each other. For standard plaque, the MC calculated dose distribution in planes parallel to the plaque is narrower than the TG43 calculation due to attenuation at the periphery of the plaque by the modulay. MC calculated the dose behind the plaque is fully attenuated. Similar results were found for the notched plaque, with asymmetric attenuation along the plane of the notch. Cumulative dose volume histograms showed significant reductions in the calculated MC doses for both tumor and eye structures, compared to TG43 calculations. The effect was most pronounced for the notch plaque where the MC dose to the optic nerve was greatly attenuated by the modulay surrounding the optic nerve compared to the TG43. Thus, a reduction of optic nerve D95% from 14 to 0.2 Gy was observed, when comparing the TG43 calculation to the MC result. The tumor D95% reduced from 89.2 to 79.95 Gy for TG43 and MC calculations, respectively. TG43 calculations overestimate the absolute dose and the lateral dose distribution of both standard and notched eye plaques, leading to the dose overestimation for the target and organs at risk. The dose matching along the central axis for the non-uniformly loaded plaques to that of uniformly loaded ones was found to be sufficient for providing comparable coverage and can be clinically used in eye-cancer-busy centers.
Keywords: Monte Carlo dosimetry; eye plaque brachytherapy; non-uniform loading; notched eye plaques.
© 2023 The Authors. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Investigation of heterogeneity corrections for accelerated Monte Carlo-based treatment planning of plaque ocular brachytherapy.Brachytherapy. 2025 Sep-Oct;24(5):754-762. doi: 10.1016/j.brachy.2025.05.004. Epub 2025 Jul 16. Brachytherapy. 2025. PMID: 40670247
-
Dosimetric and radiobiological investigation of permanent implant prostate brachytherapy based on Monte Carlo calculations.Brachytherapy. 2019 Nov-Dec;18(6):875-882. doi: 10.1016/j.brachy.2019.06.008. Epub 2019 Aug 7. Brachytherapy. 2019. PMID: 31400953
-
Evaluation of material heterogeneity dosimetric effects using radiochromic film for COMS eye plaques loaded with (125)I seeds (model I25.S16).Med Phys. 2013 Jan;40(1):011708. doi: 10.1118/1.4769423. Med Phys. 2013. PMID: 23298078
-
A Monte Carlo dose calculation system for ophthalmic brachytherapy based on a realistic eye model.Med Phys. 2021 Aug;48(8):4542-4559. doi: 10.1002/mp.15045. Epub 2021 Jul 11. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 34250607
-
Advanced Collapsed cone Engine dose calculations in tissue media for COMS eye plaques loaded with I-125 seeds.Med Phys. 2018 Jul;45(7):3349-3360. doi: 10.1002/mp.12946. Epub 2018 May 23. Med Phys. 2018. PMID: 29729009
Cited by
-
Innovations in brachytherapy.Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2025 Feb 25;15(1):62-72. doi: 10.4103/tjo.TJO-D-24-00108. eCollection 2025 Jan-Mar. Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40213297 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Thomson RM, Taylor REP, Rogers DWO. Monte Carlo dosimetry for 125I and 103Pd eye plaque brachytherapy. Med Phys. 2008;35(12):5530‐5543. - PubMed
-
- Sadeghi M, Farshadi A, Saidi P, et al. Monte Carlo Dosimetry for 125I eye plaque brachytherapy. J Nucl Med Radiat Ther. 2018;9(4):1000367.
-
- Chiu‐Tsao ST, Astrahan MA, Finger PT, et al. Dosimetry of 125I and 103Pd COMS eye plaques for intraocular tumors: report of Task Group 129 by the AAPM and ABS. Med Phys. 2012;39(10):6161‐6184. - PubMed
-
- Melhus CS. Improved eye plaque brachytherapy dosimetry using Monte Carlo methods. Nucl Technol. 2011;175(1):32‐39.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

