Hormone-induced enhancer assembly requires an optimal level of hormone receptor multivalent interactions
- PMID: 37738977
- PMCID: PMC10592010
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.08.027
Hormone-induced enhancer assembly requires an optimal level of hormone receptor multivalent interactions
Abstract
Transcription factors (TFs) activate enhancers to drive cell-specific gene programs in response to signals, but our understanding of enhancer assembly during signaling events is incomplete. Here, we show that androgen receptor (AR) forms condensates through multivalent interactions mediated by its N-terminal intrinsically disordered region (IDR) to orchestrate enhancer assembly in response to androgen signaling. AR IDR can be substituted by IDRs from selective proteins for AR condensation capacity and its function on enhancers. Expansion of the poly(Q) track within AR IDR results in a higher AR condensation propensity as measured by multiple methods, including live-cell single-molecule microscopy. Either weakening or strengthening AR condensation propensity impairs its heterotypic multivalent interactions with other enhancer components and diminishes its transcriptional activity. Our work reveals the requirement of an optimal level of AR condensation in mediating enhancer assembly and suggests that alteration of the fine-tuned multivalent IDR-IDR interactions might underlie AR-related human pathologies.
Keywords: androgen receptor; condensate formation; condensation; enhancer; hormone-induced enhancer assembly; intrinsically disordered region; multivalent interaction; phase separation.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

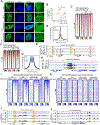
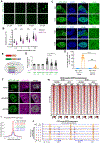
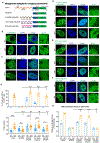



References
-
- Bi M, Zhang Z, Jiang YZ, Xue P, Wang H, Lai Z, Fu X, De Angelis C, Gong Y, Gao Z, et al. (2020). Enhancer reprogramming driven by high-order assemblies of transcription factors promotes phenotypic plasticity and breast cancer endocrine resistance. Nat Cell Biol 22, 701–715. 10.1038/s41556-020-0514-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

