Decoding Human Biology and Disease Using Single-cell Omics Technologies
- PMID: 37739168
- PMCID: PMC10928380
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gpb.2023.06.003
Decoding Human Biology and Disease Using Single-cell Omics Technologies
Abstract
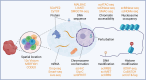
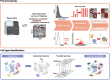
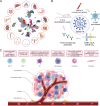
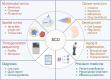
Over the past decade, advances in single-cell omics (SCO) technologies have enabled the investigation of cellular heterogeneity at an unprecedented resolution and scale, opening a new avenue for understanding human biology and disease. In this review, we summarize the developments of sequencing-based SCO technologies and computational methods, and focus on considerable insights acquired from SCO sequencing studies to understand normal and diseased properties, with a particular emphasis on cancer research. We also discuss the technological improvements of SCO and its possible contribution to fundamental research of the human, as well as its great potential in clinical diagnoses and personalized therapies of human disease.
Keywords: Cancer research; Cellular heterogeneity; Computational method; Disease; Single-cell omics.
Copyright © 2023 Beijing Institute of Genomics, Chinese Academy of Sciences / China National Center for Bioinformation and Genetics Society of China. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Zemin Zhang is a founder of Analytical BioSciences and is a board member for InnoCare Pharma. Other authors have declared no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The technological landscape and applications of single-cell multi-omics.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023 Oct;24(10):695-713. doi: 10.1038/s41580-023-00615-w. Epub 2023 Jun 6. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37280296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in bulk and single-cell multi-omics approaches for systems biology and precision medicine.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Sep 2;22(5):bbab024. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab024. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 33778867 Review.
-
Personalized analysis of human cancer multi-omics for precision oncology.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024 May 10;23:2049-2056. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2024.05.011. eCollection 2024 Dec. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 38783900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New mass spectrometry technologies contributing towards comprehensive and high throughput omics analyses of single cells.Analyst. 2019 Jan 28;144(3):794-807. doi: 10.1039/c8an01574k. Analyst. 2019. PMID: 30507980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Technological and computational advances driving high-throughput oncology.Trends Cell Biol. 2022 Nov;32(11):947-961. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2022.04.008. Epub 2022 May 13. Trends Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35577671 Review.
Cited by
-
Database Resources of the National Genomics Data Center, China National Center for Bioinformation in 2025.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jan 6;53(D1):D30-D44. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae978. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39530327 Free PMC article.
-
From Multi-omics To Personalized Training: The Rise of Enduromics and Resistomics.Sports Med Open. 2025 May 14;11(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s40798-025-00855-4. Sports Med Open. 2025. PMID: 40369313 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring T Cell and NK Cell Involvement in Ankylosing Spondylitis Through Single-Cell Sequencing.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Dec;28(24):e70206. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70206. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39680481 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liao J., Lu X., Shao X., Zhu L., Fan X. Uncovering an organ’s molecular architecture at single-cell resolution by spatially resolved transcriptomics. Trends Biotechnol. 2021;39:43–58. - PubMed
-
- Elmentaite R., Dominguez Conde C., Yang L., Teichmann S.A. Single-cell atlases: shared and tissue-specific cell types across human organs. Nat Rev Genet. 2022;23:395–410. - PubMed
-
- Buechler M.B., Pradhan R.N., Krishnamurty A.T., Cox C., Calviello A.K., Wang A.W., et al. Cross-tissue organization of the fibroblast lineage. Nature. 2021;593:575–579. - PubMed
-
- Stark R., Grzelak M., Hadfield J. RNA sequencing: the teenage years. Nat Rev Genet. 2019;20:631–656. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

