Use of non-surgical treatments on the journey to knee replacement in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a 10-year population-based case-control study
- PMID: 37739449
- PMCID: PMC10533805
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2023-003422
Use of non-surgical treatments on the journey to knee replacement in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a 10-year population-based case-control study
Abstract
Aim: To investigate temporal trends in primary care visits, physiotherapy visits, dispensed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and opioids in knee osteoarthritis (OA) patients who have and have not undergone knee replacement.
Methods: We analysed 5665 OA patients from the Skåne Healthcare Register, Sweden, who underwent knee replacement between 2015 and 2019. Controls were OA patients without knee replacement, matched 1:1 by sex, age, time and healthcare level of initial OA diagnosis, and assigned a pseudo-index date corresponding to their case's knee replacement date. Annual prevalence and prevalence ratio of primary care and physiotherapy visits, dispensed NSAIDs and opioids (all for any cause) in the 10 years before knee replacement were estimated using Poisson regression.
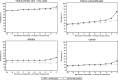
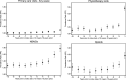
Results: The annual prevalence of all-cause primary care visits, physiotherapy visits and opioid use was similar between cases and controls until 3 years before the index date when it started to increase among the cases. The year before the index date, the prevalence ratio (cases vs controls) for physiotherapy use was 1.8 (95% CI 1.7, 1.8), while for opioid use 1.6 (1.5, 1.7). NSAID use was consistently higher among cases, even 10 years before the index date when the prevalence ratio versus controls was 1.3 (1.2, 1.3), increasing to 1.8 (1.7, 1.9) in the year preceding the index date.
Conclusions: Management of OA patients who have and have not undergone knee replacement appears largely similar except for higher use of NSAIDs in knee replacement cases. Symptomatic treatments start to increase a few years before the surgery in knee replacement cases.
Keywords: Epidemiology; Osteoarthritis, Knee; Rehabilitation.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Frequent use of prescription NSAIDs among people with knee or hip osteoarthritis despite contraindications to or precautions with NSAIDs.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2024 Dec;32(12):1628-1635. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2024.07.010. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2024. PMID: 39068982
-
Opioid use prior to total knee replacement: comparative analysis of trends in England and Sweden.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022 Jun;30(6):815-822. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2022.02.621. Epub 2022 Mar 17. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022. PMID: 35307536
-
Intra-articular viscosupplementation with hylan g-f 20 to treat osteoarthritis of the knee: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2005;5(10):1-66. Epub 2005 Jun 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2005. PMID: 23074461 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment modalities for hip and knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review of safety.J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2018 May-Aug;26(3):2309499018808669. doi: 10.1177/2309499018808669. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2018. PMID: 30415598
-
American College of Rheumatology 2012 recommendations for the use of nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic therapies in osteoarthritis of the hand, hip, and knee.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012 Apr;64(4):465-74. doi: 10.1002/acr.21596. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012. PMID: 22563589 Review.
Cited by
-
Change in willingness for surgery and risk of joint replacement after an education and exercise program for hip/knee osteoarthritis: A longitudinal cohort study of 55,059 people.PLoS Med. 2025 May 8;22(5):e1004577. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004577. eCollection 2025 May. PLoS Med. 2025. PMID: 40338890 Free PMC article.
-
Frequent use of prescription NSAIDs among people with knee or hip osteoarthritis despite contraindications to or precautions with NSAIDs.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2024 Dec;32(12):1628-1635. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2024.07.010. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2024. PMID: 39068982
References
-
- Socialstyrelsen . Nationella Riktlinjer För Rörelseorganens Sjukdomar. Reumatoid Artrit, axial Spondylartrit, Psoriasisartrit, Artros och Osteoporos. Socialstyrelsen Stockholm 2021.
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) . Osteoarthritis in over 16S: diagnosis and management. NICE Guideline NG226 2022. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
