The Impact of Cerebral Ischemia on Antioxidant Enzymes Activity and Neuronal Damage in the Hippocampus
- PMID: 37740074
- PMCID: PMC11407731
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-023-01413-w
The Impact of Cerebral Ischemia on Antioxidant Enzymes Activity and Neuronal Damage in the Hippocampus
Abstract
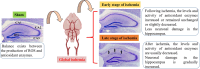
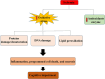
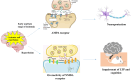
Cerebral ischemia and subsequent reperfusion, leading to reduced blood supply to specific brain areas, remain significant contributors to neurological damage, disability, and mortality. Among the vulnerable regions, the subcortical areas, including the hippocampus, are particularly susceptible to ischemia-induced injuries, with the extent of damage influenced by the different stages of ischemia. Neural tissue undergoes various changes and damage due to intricate biochemical reactions involving free radicals, oxidative stress, inflammatory responses, and glutamate toxicity. The consequences of these processes can result in irreversible harm. Notably, free radicals play a pivotal role in the neuropathological mechanisms following ischemia, contributing to oxidative stress. Therefore, the function of antioxidant enzymes after ischemia becomes crucial in preventing hippocampal damage caused by oxidative stress. This study explores hippocampal neuronal damage and enzymatic antioxidant activity during ischemia and reperfusion's early and late stages.
Keywords: Antioxidant enzymes; Cerebral ischemia; Hippocampus; Neuronal damage; Oxidative stress.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Adedara IA, Owumi SE, Oyelere AK, Farombi EO (2021) Neuroprotective role of gallic acid in aflatoxin B1-induced behavioral abnormalities in rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 35(3):e22684 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

