Long COVID quality of life and healthcare experiences in the UK: a mixed method online survey
- PMID: 37740144
- PMCID: PMC10784347
- DOI: 10.1007/s11136-023-03513-y
Long COVID quality of life and healthcare experiences in the UK: a mixed method online survey
Abstract
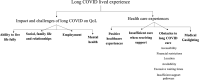
Purpose: The complexity of long COVID and its diverse symptom profile contributes to unprecedented challenges for patients, clinicians, and healthcare services. The threat of long COVID remains ignored by Governments, the media and public health messaging, and patients' experiences must be heard through understanding of the lived experience. This study aimed to understand the lived experience of those living with long COVID.
Methods: An online web-based survey was designed using Patient and Public Involvement and Engagement (PPIE) to increase understanding of the lived experiences of long COVID, and was distributed through PPIE groups, social media, and word of mouth. The survey used closed and open questions relating to demographics, pre- and post-COVID-19 health quality of life, daily activities and long COVID experiences.
Results: Within our sample of 132 people living with long COVID, the findings highlight that individuals are being severely impacted by their symptoms and are unable to or limited in participating in their daily activities, reducing quality of life. Long COVID places strain on relationships, the ability to live life fully and is detrimental to mental health. Varying health care experiences are described by participants, with reports of medical gaslighting and inadequate support received.
Conclusions: Long COVID has a severe impact on the ability to live life fully, and strains mental health. The appropriate mechanisms and support services are needed to support those living with long COVID and manage symptoms.
Keywords: Long COVID; Morbidity; Pandemic; Patient and public involvement and engagement (PPIE); Public health.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Organisation WH. Post COVID-19 Condition Clinical Case Definition 2021. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-Post_COVID-19_cond...
-
- Faghy MA, Maden-Wilkinson T, Arena R, Copeland RJ, Owen R, Hodgkins H, Willmott A. COVID-19 patients require multi-disciplinary rehabilitation approaches to address persisting symptom profiles and restore pre-COVID quality of life. Expert Review of Respiratory Medicine. 2022;16:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Statistics OfN. Prevalence of ongoing symptoms following coronavirus (COVID-19) infection in the UK: 7 July 2022 2022 [20/07/22]. Retrieved from https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/healthandsocialcare/...
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical