DSCC1 interacts with HSP90AB1 and promotes the progression of lung adenocarcinoma via regulating ER stress
- PMID: 37742009
- PMCID: PMC10518103
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-023-03047-w
DSCC1 interacts with HSP90AB1 and promotes the progression of lung adenocarcinoma via regulating ER stress
Abstract
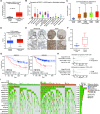
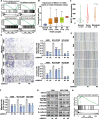
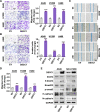
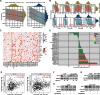
Lung cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths, and the most common type is lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). LUAD is frequently diagnosed in people who never smoked, patients are always diagnosed at advanced inoperable stages, and the prognosis is ultimately poor. Thus, there is an urgent need for the development of novel targeted therapeutics to suppress LUAD progression. In this study, we demonstrated that the expression of DNA replication and sister chromatid cohesion 1 (DSCC1) was higher in LUAD samples than normal tissues, and the overexpression of DSCC1 or its coexpressed genes were highly correlated with poor outcomes of LUAD patients, highlighting DSCC1 might be involved in LUAD progression. Furthermore, the expression of DSCC1 was positively correlated with multiple genetic mutations which drive cancer development, including TP53, TTN, CSMD, and etc. More importantly, DSCC1 could promote the cell proliferation, stemness, EMT, and metastatic potential of LUAD cells. In addition, DSCC1 interacted with HSP90AB1 and promoted the progression of LUAD via regulating ER stress. Meanwhile, DSCC1 expression negatively correlated with immune cell infiltration in lung cancer, and DSCC1 positively regulated the expression of PD-L1 in LUAD cells. Collectively, this study revealed that DSCC1 is a novel therapeutic target to treat LUAD and a biomarker for predicting the efficiency of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade treatment.
Keywords: DSCC1; HSP90AB1; Lung adenocarcinoma; Metastasis; PD-L1; Proliferation; Stemness.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest exits in the submission of this manuscript.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Decoding the DSCC1 gene as a pan-cancer biomarker in human cancers via comprehensive multi-omics analyses.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Mar 15;16(3):738-754. doi: 10.62347/YORR3755. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38586115 Free PMC article.
-
High DSCC1 Level Predicts Poor Prognosis of Lung Adenocarcinoma.Int J Gen Med. 2021 Oct 20;14:6961-6974. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S329482. eCollection 2021. Int J Gen Med. 2021. PMID: 34707388 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Upregulated DNA Replication and Sister Chromatid Cohesion 1 Expression on Proliferation and Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Chin Med J (Engl). 2018 Dec 5;131(23):2827-2835. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.246076. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018. PMID: 30511685 Free PMC article.
-
AIM2 upregulation promotes metastatic progression and PD-L1 expression in lung adenocarcinoma.Cancer Sci. 2023 Jan;114(1):306-320. doi: 10.1111/cas.15584. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Cancer Sci. 2023. PMID: 36104978 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the prognostic, diagnostic, and immunological roles of DSCC1 and its genomic alteration and instability in human cancers.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2024 Apr 28;70(4):202-211. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2024.70.4.32. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2024. PMID: 38678604
Cited by
-
GLCCI1 alleviates GRP78-initiated endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis of retinal ganglion cells in diabetic retinopathy by upregulating and interacting with HSP90AB1.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 4;14(1):26665. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75874-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39496608 Free PMC article.
-
Complementary biomarkers of computed tomography for diagnostic grading of gastric cancer: DSCC1 and GINS1.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Jan 31;16(5):4149-4168. doi: 10.18632/aging.205491. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38301047 Free PMC article.
-
Vortioxetine exhibits anti-glioblastoma activity via the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025;28(4):401-408. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2025.82513.17836. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39968089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of multiomics and immune infiltration-associated biomarkers for early gastric cancer: a machine learning-based diagnostic model development study.BMC Cancer. 2025 May 31;25(1):972. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14396-2. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40450287 Free PMC article.
-
HNRNPH1 promotes autophagy to inhibit the development of lung adenocarcinoma via the HSP90AB1/MAP1LC3B axis.Respir Res. 2025 Jun 4;26(1):206. doi: 10.1186/s12931-025-03280-z. Respir Res. 2025. PMID: 40468317 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang J, Chen A, Xue Z, Liang C. Identification of immune-associated prognostic biomarkers in lung adenocarcinoma on the basis of gene co-expression network. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2022;1–30. 10.1080/08923973.2022.2145965. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- JBZX-202007/Research Center for Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment Technology in Zhejiang Province
- JBZX-202007/Research Center for Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment Technology in Zhejiang Province
- JBZX-202007/Research Center for Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment Technology in Zhejiang Province
- JBZX-202007/Research Center for Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment Technology in Zhejiang Province
- JBZX-202007/Research Center for Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment Technology in Zhejiang Province
- 2020C03058/Zhejiang Province Major Science and Technology Special Plan Project
- 2020C03058/Zhejiang Province Major Science and Technology Special Plan Project
- 2020C03058/Zhejiang Province Major Science and Technology Special Plan Project
- 2020C03058/Zhejiang Province Major Science and Technology Special Plan Project
- LGF21H310002/Public-service Technology Research Plan of Zhejiang Province
- LGF21H310002/Public-service Technology Research Plan of Zhejiang Province
- LGF21H310002/Public-service Technology Research Plan of Zhejiang Province
- LGF21H310002/Public-service Technology Research Plan of Zhejiang Province
- LGF21H310002/Public-service Technology Research Plan of Zhejiang Province
- LGF21H310002/Public-service Technology Research Plan of Zhejiang Province
- LHDMY22H160001/Huadong Medicine Joint Funds of the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- LHDMY22H160001/Huadong Medicine Joint Funds of the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- LHDMY22H160001/Huadong Medicine Joint Funds of the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- LHDMY22H160001/Huadong Medicine Joint Funds of the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- LHDMY22H160001/Huadong Medicine Joint Funds of the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- LY21H160017/Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation
- 82273352/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2021RC104/Zhejiang Provincial Medical and Health Technology Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

